Glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit gene family
- PMID: 19700406
- PMCID: PMC2785553
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R109.025544
Glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit gene family
Abstract
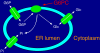
Glucose-6-phosphatase catalyzes the hydrolysis of glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) to glucose and inorganic phosphate. It is a multicomponent system located in the endoplasmic reticulum that comprises several integral membrane proteins, namely a catalytic subunit (G6PC) and transporters for G6P, inorganic phosphate, and glucose. The G6PC gene family contains three members, designated G6PC, G6PC2, and G6PC3. The tissue-specific expression patterns of these genes differ, and mutations in all three genes have been linked to distinct diseases in humans. This minireview discusses the disease association and transcriptional regulation of the G6PC genes as well as the biological functions of the encoded proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Mithieux G. (1997) Eur. J. Endocrinol. 136, 137–145 - PubMed
-
- Foster J. D., Pederson B. A., Nordlie R. C. (1997) Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 215, 314–332 - PubMed
-
- Lei K. J., Shelly L. L., Pan C. J., Sidbury J. B., Chou J. Y. (1993) Science 262, 580–583 - PubMed
-
- Shelly L. L., Lei K. J., Pan C. J., Sakata S. F., Ruppert S., Schutz G., Chou J. Y. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268, 21482–21485 - PubMed
-
- Lei K. J., Chen H., Pan C. J., Ward J. M., Mosinger B., Jr., Lee E. J., Westphal H., Mansfield B. C., Chou J. Y. (1996) Nat. Genet. 13, 203–209 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK057516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076027/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK052068/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56374/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK57516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK052068/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK076027/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK061645/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056374/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK76027/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052068/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK61645/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

