Identification of flagellar motility genes in Yersinia ruckeri by transposon mutagenesis
- PMID: 19700548
- PMCID: PMC2765149
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01415-09
Identification of flagellar motility genes in Yersinia ruckeri by transposon mutagenesis
Abstract
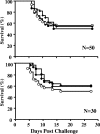
Here we demonstrate that flagellar secretion is required for production of secreted lipase activity in the fish pathogen Yersinia ruckeri and that neither of these activities is necessary for virulence in rainbow trout. Our results suggest a possible mechanism for the emergence of nonmotile biotype 2 Y. ruckeri through the mutational loss of flagellar secretion.
Figures



References
-
- Arias, C. R., O. Olivares-Fuster, K. Hayden, C. A. Shoemaker, J. M. Grizzle, and P. H. Klesius. 2007. First report of Yersinia ruckeri biotype 2 in the USA. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 19:35-40. - PubMed
-
- Austin, D. A., P. A. Robertson, and B. Austin. 2003. Recovery of a new biogroup of Yersinia ruckeri from diseased rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 26:127-131. - PubMed
-
- Busch, R. A. 1978. Enteric red mouth disease (Hagerman strain). Mar. Fish Rev. 40:467-472.
-
- Conchas, R. F., and E. Carniel. 1990. A highly efficient electroporation system for transformation of Yersinia. Gene 87:133-137. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

