Mechanism-based inactivation of CYP2B1 and its F-helix mutant by two tert-butyl acetylenic compounds: covalent modification of prosthetic heme versus apoprotein
- PMID: 19700628
- PMCID: PMC2775271
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.158782
Mechanism-based inactivation of CYP2B1 and its F-helix mutant by two tert-butyl acetylenic compounds: covalent modification of prosthetic heme versus apoprotein
Abstract
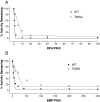
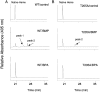
The mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome CYP2B1 [wild type (WT)] and its Thr205 to Ala mutant (T205A) by tert-butylphenylacetylene (BPA) and tert-butyl 1-methyl-2-propynyl ether (BMP) in the reconstituted system was investigated. The inactivation of WT by BPA exhibited a k(inact)/K(I) value of 1343 min(-1)mM(-1) and a partition ratio of 1. The inactivation of WT by BMP exhibited a k(inact)/K(I) value of 33 min(-1)mM(-1) and a partition ratio of 10. Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry analysis (LC/MS/MS) of the WT revealed 1) inactivation by BPA resulted in the formation of a protein adduct with a mass increase equivalent to the mass of BPA plus one oxygen atom, and 2) inactivation by BMP resulted in the formation of multiple heme adducts that all exhibited a mass increase equivalent to BMP plus one oxygen atom. LC/MS/MS analysis indicated the formation of glutathione (GSH) conjugates by the reaction of GSH with the ethynyl moiety of BMP or BPA with the oxygen being added to the internal or terminal carbon. For the inactivation of T205A by BPA and BMP, the k(inact)/K(I) values were suppressed by 100- and 4-fold, respectively, and the partition ratios were increased 9- and 3.5-fold, respectively. Only one major heme adduct was detected following the inactivation of the T205A by BMP. These results show that the Thr205 in the F-helix plays an important role in the efficiency of the mechanism-based inactivation of CYP2B1 by BPA and BMP. Homology modeling and substrate docking studies were presented to facilitate the interpretation of the experimental results.
Figures
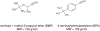
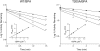


References
-
- Baillie TA, Davis MR. (1993) Mass spectrometry in the analysis of glutathione conjugates. Biol Mass Spectrom 22:319–325 - PubMed
-
- Blobaum AL, Kent UM, Alworth WL, Hollenberg PF. (2002) Mechanism-based inactivation of cytochromes P450 2E1 and 2E1 T303A by tert-butyl acetylenes: characterization of reactive intermediate adducts to the heme and apoprotein. Chem Res Toxicol 15:1561–1571 - PubMed
-
- CaJacob CA, Chan WK, Shephard E, Ortiz de Montellano PR. (1988) The catalytic site of rat hepatic lauric acid ω-hydroxylase: protein versus prosthetic heme alkylation in the ω-hydroxylation of acetylenic fatty acids. J Biol Chem 263:18640–18649 - PubMed
-
- Chan WK, Sui Z, Ortiz de Montellano PR. (1993) Determinants of protein modification versus heme alkylation: inactivation of cytochrome P450 1A1 by 1-ethynylpyrene and phenylacetylene. Chem Res Toxicol 6:38–45 - PubMed
-
- Domanski TL, Halpert JR. (2001) Analysis of mammalian cytochrome P450 structure and function by site-directed mutagenesis. Curr Drug Metab 2:117–137 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

