An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase formed by TERT and the RMRP RNA
- PMID: 19701182
- PMCID: PMC2755635
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08283
An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase formed by TERT and the RMRP RNA
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase formed by TERT and the RMRP RNA.Nature. 2025 Feb;638(8050):E3. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08559-7. Nature. 2025. PMID: 39875610 No abstract available.
Abstract
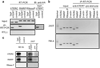
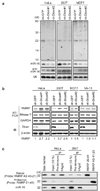
Constitutive expression of telomerase in human cells prevents the onset of senescence and crisis by maintaining telomere homeostasis. However, accumulating evidence suggests that the human telomerase reverse transcriptase catalytic subunit (TERT) contributes to cell physiology independently of its ability to elongate telomeres. Here we show that TERT interacts with the RNA component of mitochondrial RNA processing endoribonuclease (RMRP), a gene that is mutated in the inherited pleiotropic syndrome cartilage-hair hypoplasia. Human TERT and RMRP form a distinct ribonucleoprotein complex that has RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) activity and produces double-stranded RNAs that can be processed into small interfering RNA in a Dicer (also known as DICER1)-dependent manner. These observations identify a mammalian RdRP composed of TERT in complex with RMRP.
Figures



References
-
- Cohen SB, et al. Protein composition of catalytically active human telomerase from immortal cells. Science. 2007;315:1850–1853. - PubMed
-
- Weinrich SL, et al. Reconstitution of human telomerase with the template RNA component hTR and the catalytic protein subunit hTRT. Nat. Genet. 1997;17:498–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

