A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses
- PMID: 19701202
- PMCID: PMC3034219
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2015
A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses
Abstract
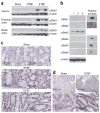
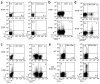
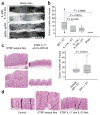
The intestinal flora may promote colon tumor formation. Here we explore immunologic mechanisms of colonic carcinogenesis by a human colonic bacterium, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF). ETBF that secretes B. fragilis toxin (BFT) causes human inflammatory diarrhea but also asymptomatically colonizes a proportion of the human population. Our results indicate that whereas both ETBF and nontoxigenic B. fragilis (NTBF) chronically colonize mice, only ETBF triggers colitis and strongly induces colonic tumors in multiple intestinal neoplasia (Min) mice. ETBF induces robust, selective colonic signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (Stat3) activation with colitis characterized by a selective T helper type 17 (T(H)17) response distributed between CD4+ T cell receptor-alphabeta (TCRalphabeta)+ and CD4-8-TCRgammadelta+ T cells. Antibody-mediated blockade of interleukin-17 (IL-17) as well as the receptor for IL-23, a key cytokine amplifying T(H)17 responses, inhibits ETBF-induced colitis, colonic hyperplasia and tumor formation. These results show a Stat3- and T(H)17-dependent pathway for inflammation-induced cancer by a common human commensal bacterium, providing new mechanistic insight into human colon carcinogenesis.
Figures
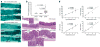
Comment in
-
STAT3 implicated in the development of colon cancer: a step closer for targeted therapy?Gastroenterology. 2010 Jul;139(1):353-5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.05.030. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20639089 No abstract available.
References
-
- Suerbaum S, Michetti P. Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1175–1186. - PubMed
-
- El Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–2576. - PubMed
-
- Greten FR, et al. IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell. 2004;118:285–296. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Greten FR. NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:749–759. - PubMed
-
- Naugler WE, et al. Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science. 2007;317:121–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 CA062924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK064388/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK045496/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 HD44355/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR00171/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK45496/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI089830/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD044355/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 2 T32GM066691/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM066691/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080817/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK64388/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK079509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K26 RR000171/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

