Functional study of the effect of phosphatase inhibitors on KCNQ4 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- PMID: 19701239
- PMCID: PMC4007189
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.117
Functional study of the effect of phosphatase inhibitors on KCNQ4 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes
Abstract
Aim: KCNQ4 channels play an important part in adjusting the function of cochlear outer hair cells. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of ser/thr phosphatase inhibitors on human KCNQ4 channels expressed in Xenopuslaevis oocytes.
Methods: Synthetic cRNA encoding human KCNQ4 channels was injected into Xenopus oocytes. We used a two-electrode voltage clamp to measure the ion currents in the oocytes.
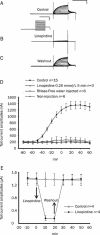
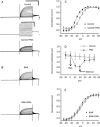
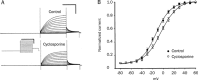
Results: Wild-type KCNQ4 expressed in Xenopus oocytes showed the typical properties of slow activation kinetics and low threshold activation. The outward K(+) current was almost completely blocked by a KCNQ4 blocker, linopirdine (0.25 mmol/L). BIMI (a PKC inhibitor) prevented the effects of PMA (a PKC activator) on the KCNQ4 current, indicating that PKC may be involved in the regulation of KCNQ4 expressed in the Xenopus oocyte system. Treatment with the ser/thr phosphatase inhibitors, cyclosporine (2 micromol/L), calyculin A (2 micromol/L) or okadaic acid (1 micromol/L), caused a significant positive shift in V(1/2) and a decrease in the conductance of KCNQ4 channels. The V(1/2) was shifted from -14.6+/-0.5 to -6.4+/-0.4 mV by cyclosporine, -18.8+/-0.5 to -9.2+/-0.4 mV by calyculin A, and -14.1+/-0.5 to -0.7+/-0.6 mV by okadaic acid. Moreover, the effects of these phosphatase inhibitors (okadaic acid or calyculin A) on the induction of a positive shift of V(1/2) were augmented by further addition of PMA.
Conclusion: These results indicate that ser/thr phosphatase inhibitors can induce a shift to more positive potentials of the activation curve of the KCNQ4 current. It is highly likely that the phosphatase functions to balance the phosphorylated state of substrate protein and thus has an important role in the regulation of human KCNQ4 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Kubisch C, Schroeder BC, Friedrich T, Lutjohann B, El-Amraoui A, Marlin S, et al. KCNQ4, a novel potassium channel expressed in sensory outer hair cells is, mutated in dominant deafness. Cell. 1999;96:437–46. - PubMed
-
- Gutman GA, Chandy KG, Adelman JP, Aiyar J, Bayliss DA, Clapham DE, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XLI. Compendium of voltage-gated ion channels: potassium channels. Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55:583–6. - PubMed
-
- Marrion NV. Control of M-current. Annu Rev Physiol. 1997;59:483–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

