Parenting practices and problem behavior across three generations: monitoring, harsh discipline, and drug use in the intergenerational transmission of externalizing behavior
- PMID: 19702387
- PMCID: PMC2766356
- DOI: 10.1037/a0016129
Parenting practices and problem behavior across three generations: monitoring, harsh discipline, and drug use in the intergenerational transmission of externalizing behavior
Abstract
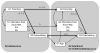
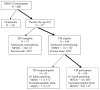
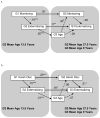
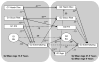
Using data from grandparents (G1), parents (G2), and children (G3), this study examined continuity in parental monitoring, harsh discipline, and child externalizing behavior across generations, and the contribution of parenting practices and parental drug use to intergenerational continuity in child externalizing behavior. Structural equation and path modeling of prospective, longitudinal data from 808 G2 participants, their G1 parents, and their school-age G3 children (n = 136) showed that parental monitoring and harsh discipline demonstrated continuity from G1 to G2. Externalizing behavior demonstrated continuity from G2 to G3. Continuity in parenting practices did not explain the intergenerational continuity in externalizing behavior. Rather, G2 adolescent externalizing behavior predicted their adult substance use, which was associated with G3 externalizing behavior. A small indirect effect of G1 harsh parenting on G3 was observed. Interparental abuse and socidemographic risk were included as controls but did not explain the intergenerational transmission of externalizing behavior. Results highlight the need for preventive interventions aimed at breaking intergenerational cycles in poor parenting practices. More research is required to identify parental mechanisms influencing the continuity of externalizing behavior across generations.
Figures
Comment in
-
The intergenerational transmission of parenting: closing comments for the special section.Dev Psychol. 2009 Sep;45(5):1276-83. doi: 10.1037/a0016911. Dev Psychol. 2009. PMID: 19702391
References
-
- Achenbach TM, Edelbrock C. Manual for the Teacher’s Report Form and Teacher Version of the Child Behavior Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont Press; 1986.
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms & Profiles. Burlington: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families; 2001.
-
- Akers RL. Deviant behavior: A social learning approach. 2. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth; 1977.
-
- Bailey JA, Hill KG, Oesterle S, Hawkins JD. Linking substance use and problem behavior across three generations. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 2006;34:273–292. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A. Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review. 1977;84:191–215. - PubMed

