From mitochondrial dynamics to arrhythmias
- PMID: 19703656
- PMCID: PMC2732583
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.02.016
From mitochondrial dynamics to arrhythmias
Abstract
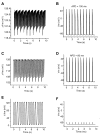
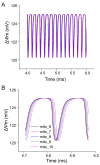
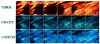
The reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent mitochondrial oscillator described in cardiac cells exhibits at least two modes of function under physiological conditions or in response to metabolic and oxidative stress. Both modes depend upon network behavior of mitochondria. Under physiological conditions cardiac mitochondria behave as a network of coupled oscillators with a broad range of frequencies. ROS weakly couples mitochondria under normal conditions but becomes a strong coupling messenger when, under oxidative stress, the mitochondrial network attains criticality. Mitochondrial criticality is achieved when a threshold of ROS is overcome and a certain density of mitochondria forms a cluster that spans the whole cell. Under these conditions, the slightest perturbation triggers a cell-wide collapse of the mitochondrial membrane potential, Delta psi(m), visualized as a depolarization wave throughout the cell which is followed by whole cell synchronized oscillations in Delta psi(m), NADH, ROS, and GSH. This dynamic behavior scales from the mitochondrion to the cell by driving cellular excitability and the whole heart into catastrophic arrhythmias. A network collapse of Delta psi(m) under criticality leads to: (i) energetic failure, (ii) temporal and regional alterations in action potential (AP), (iii) development of zones of impaired conduction in the myocardium, and, ultimately, (iv) a fatal ventricular arrhythmia.
Figures


References
-
- Aon MA, Cortassa S. Chaotic dynamics, noise and fractal space in biochemistry. In: Meyers R, editor. Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science. New York: Springer; 2009.
-
- Aon MA, Cortassa S, Marban E, O’Rourke B. Synchronized whole cell oscillations in mitochondrial metabolism triggered by a local release of reactive oxygen species in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:44735–44744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

