Effects of antipsychotic drugs on MK-801-induced attentional and motivational deficits in rats
- PMID: 19705572
- PMCID: PMC2775532
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.01.004
Effects of antipsychotic drugs on MK-801-induced attentional and motivational deficits in rats
Abstract
Background: Attentional deficits that accompany schizophrenia are not effectively treated by available antipsychotic medications. Disruption of NMDA receptor function is often used to model aspects of this disorder in rodents. We used the 5-choice serial reaction time task (5CSRTT) to characterize attentional deficits caused by acute administration or withdrawal from chronic administration of the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801, and determine if they are ameliorated by haloperidol or clozapine.
Methods: Acute studies involved tests in the presence of MK-801: rats were administered haloperidol (0.008-0.125 mg/kg, SC) or clozapine (0.16-2.5 mg/kg, SC) in combination with MK-801 (0.25 mg/kg, IP) prior to daily test sessions. Chronic studies involved tests in the absence of MK-801: following daily tests, rats were administered MK-801 (0.5 mg/kg, IP) and tested 24 h later in the absence or presence of haloperidol or clozapine.
Results: Acute MK-801 disrupted performance: it decreased accuracy while increasing omissions, premature responses, and magazine entries. Haloperidol reduced disruptive effects associated with increased activation, whereas it exacerbated other deficits. Clozapine dose-dependently attenuated several of the MK-801-induced performance deficits. Withdrawal from chronic MK-801 progressively increased omissions and response latencies and decreased premature responding, suggesting an amotivational state. Neither haloperidol nor clozapine ameliorated these performance deficits.
Discussion: Acute administration and withdrawal from chronic MK-801 administration produced distinct behavioral profiles in the 5CSRTT. Acute MK-801 impaired attention and impulse control whereas chronic MK-801 withdrawal caused signs consistent with amotivation. Haloperidol and clozapine were more effective at attenuating deficits caused by acute MK-801 administration.
Figures

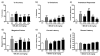

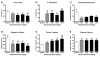

References
-
- Abdul-Monim Z, Reynolds GP, Neill JC. The effect of atypical and classical antipsychotics on sub-chronic PCP-induced cognitive deficits in a reversal-learning paradigm. Behavioural Brain Research. 2006;169:263–273. - PubMed
-
- Amitai N, Semenova S, Markou A. Cognitive-disruptive effects of the psychotomimetic phencyclidine and attenuation by atypical antipsychotic medications in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2007;193:521–537. - PubMed
-
- Baviera M, Invernizzi RW, Carli M. Haloperidol and clozapine have dissociable effects in a model of attentional performance deficits induced by blockade of NMDA receptors in the mPFC. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2008;196:269–280. - PubMed
-
- Benaliouad F, Kapur S, Rompré PP. Blockade of 5-HT2a receptors reduces haloperidol-induced attenuation of reward. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007;32:551–561. - PubMed
-
- Behrens MM, Ali SS, Dao DN, Lucero J, Shekhtman G, Quick KL, Dugan LL. Ketamine-induced loss of phenotype of fast-spiking interneurons is mediated by NADPH-oxidase. Science. 2007;318:1645–1647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
