Hsp-27 expression at diagnosis predicts poor clinical outcome in prostate cancer independent of ETS-gene rearrangement
- PMID: 19707199
- PMCID: PMC2768089
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605227
Hsp-27 expression at diagnosis predicts poor clinical outcome in prostate cancer independent of ETS-gene rearrangement
Abstract
Background: This study was performed to test the hypothesis that expression of small heat shock protein Hsp-27 is, at diagnosis, a reliable predictive biomarker of clinically aggressive prostate cancer.
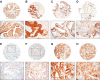
Methods: A panel of tissue microarrays constructed from a well-characterised cohort of 553 men with conservatively managed prostate cancer was stained immunohistochemically to detect Hsp-27 protein. Hsp-27 expression was compared with a series of pathological and clinical parameters, including outcome.
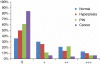
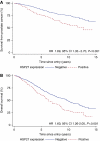
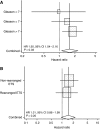
Results: Hsp-27 staining was indicative of higher Gleason score (P<0.001). In tissue cores having a Gleason score >7, the presence of Hsp-27 retained its power to independently predict poor clinical outcome (P<0.002). Higher levels of Hsp-27 staining were almost entirely restricted to cancers lacking ERG rearrangements (chi2 trend=31.4, P<0.001), although this distribution did not have prognostic significance.
Interpretation: This study has confirmed that, in prostate cancers managed conservatively over a period of more than 15 years, expression of Hsp-27 is an accurate and independent predictive biomarker of aggressive disease with poor clinical outcome (P<0.001). These findings suggest that apoptotic and cell-migration pathways modulated by Hsp-27 may contain targets susceptible to the development of biologically appropriate chemotherapeutic agents that are likely to prove effective in treating aggressive prostate cancers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heat shock protein expression independently predicts clinical outcome in prostate cancer.Cancer Res. 2000 Dec 15;60(24):7099-105. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 11156417
-
Characterization of 1577 primary prostate cancers reveals novel biological and clinicopathologic insights into molecular subtypes.Eur Urol. 2015 Oct;68(4):555-67. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.04.033. Epub 2015 May 8. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25964175 Free PMC article.
-
Association between DNA methylation of HSPB1 and death in low Gleason score prostate cancer.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013 Mar;16(1):35-40. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2012.47. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013. PMID: 23165430 Free PMC article.
-
ETS rearrangements in prostate cancer.Asian J Androl. 2012 May;14(3):393-9. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.145. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Asian J Androl. 2012. PMID: 22504874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Dangerous liaisons in prostate cancer. Clinical and biological implications of recurrent gene fusions].Pathologe. 2010 Oct;31 Suppl 2:121-5. doi: 10.1007/s00292-010-1345-7. Pathologe. 2010. PMID: 20798944 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Exploiting Interdata Relationships in Prostate Cancer Proteomes: Clinical Significance of HO-1 Interactors.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 31;11(2):290. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020290. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204174 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein 27: a potential biomarker of peritoneal metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer?Tumour Biol. 2014 Feb;35(2):1051-6. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1139-7. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24061637
-
Molecular markers for prostate cancer in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:283635. doi: 10.1155/2013/283635. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24371818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohistochemical detection of HSP27 and hnRNP K as prognostic and predictive biomarkers for colorectal cancer.Med Oncol. 2012 Sep;29(3):1780-8. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-0037-3. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21861207
-
Quantitative proteomic determination of diethylstilbestrol action on prostate cancer.Asian J Androl. 2013 May;15(3):413-20. doi: 10.1038/aja.2012.128. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Asian J Androl. 2013. PMID: 23435471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams DJ, Hajj H, Edwards DP, Bjercke RJ, McGuire WL (1983) Detection of a Mr 24,000 estrogen-regulated protein in human breast cancer by monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res 43: 4297–4301 - PubMed
-
- Adolfsson J, Steineck G, Hedlund P-O (1997) Deferred treatment of clinically localized low-grade prostate cancer: actual 10-year and projected 15-year follow-up of the Karolinska series. Urology 50: 722–726 - PubMed
-
- Albertsen P, Hanley JA, Fine J (2005) 20-year outcomes following conservative management of clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA 293: 2095–2101 - PubMed
-
- Albertsen PC, Fryback DG, Storer BE, Kolon TF, Fine J (1995) Long-term survival among men with conservatively treated localized prostate cancer. JAMA 274: 626–631 - PubMed
-
- Attard G, Clark J, Ambroisine L, Fisher G, Kovacs G, Flohr P, Berney D, Foster CS, Fletcher A, Gerald WL, Moller H, Reuter V, De Bono JS, Scardino P, Cuzick J, Cooper CS (2008a) Duplication of the fusion of TMPRSS2 to ERG sequences identifies fatal human prostate cancer. Oncogene 27: 253–263 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

