Recognition of handwriting from electromyography
- PMID: 19707562
- PMCID: PMC2727961
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006791
Recognition of handwriting from electromyography
Abstract
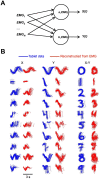
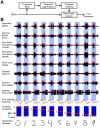
Handwriting--one of the most important developments in human culture--is also a methodological tool in several scientific disciplines, most importantly handwriting recognition methods, graphology and medical diagnostics. Previous studies have relied largely on the analyses of handwritten traces or kinematic analysis of handwriting; whereas electromyographic (EMG) signals associated with handwriting have received little attention. Here we show for the first time, a method in which EMG signals generated by hand and forearm muscles during handwriting activity are reliably translated into both algorithm-generated handwriting traces and font characters using decoding algorithms. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of recreating handwriting solely from EMG signals - the finding that can be utilized in computer peripherals and myoelectric prosthetic devices. Moreover, this approach may provide a rapid and sensitive method for diagnosing a variety of neurogenerative diseases before other symptoms become clear.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Birbaumer N, Murguialday AR, Cohen L. Brain-computer interface in paralysis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008;21:634–638. - PubMed
-
- Lebedev MA, Nicolelis MA. Brain-machine interfaces: past, present and future. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:536–546. - PubMed
-
- Ohnishi K, Weir RF, Kuiken TA. Neural machine interfaces for controlling multifunctional powered upper-limb prostheses. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2007;4:43–53. - PubMed
-
- Parker P, Englehart K, Hudgins B. Myoelectric signal processing for control of powered limb prostheses. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2006;16:541–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

