Procaspase-3 activation as an anti-cancer strategy: structure-activity relationship of procaspase-activating compound 1 (PAC-1) and its cellular co-localization with caspase-3
- PMID: 19708658
- PMCID: PMC2749958
- DOI: 10.1021/jm900722z
Procaspase-3 activation as an anti-cancer strategy: structure-activity relationship of procaspase-activating compound 1 (PAC-1) and its cellular co-localization with caspase-3
Abstract
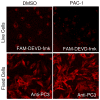
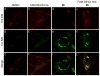
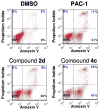
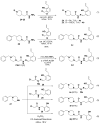
A goal of personalized medicine as applied to oncology is to identify compounds that exploit a defined molecular defect in a cancerous cell. A compound called procaspase-activating compound 1 (PAC-1) was reported that enhances the activity of procaspase-3 in vitro and induces apoptotic death in cancer cells in culture and in mouse xenograft models. Experimental evidence indicates that PAC-1 activates procaspase-3 in vitro through chelation of inhibitory zinc ions. Described herein is the synthesis and biological activity of a family of PAC-1 derivatives where key functional groups have been systematically altered. Analysis of these compounds reveals a strong correlation between the in vitro procaspase-3 activating effect and their ability to induce death in cancer cells in culture. Importantly, we also show that a fluorescently labeled version of PAC-1 co-localizes with sites of caspase-3 activity in cancer cells. The data presented herein further bolster the hypothesis that PAC-1 induces apoptosis in cancer cells through the direct activation of procaspase-3, has implications for the design and discovery of next-generation procaspase-3 activating compounds, and sheds light on the anti-apoptotic role of cellular zinc.
Figures



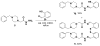
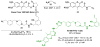
References
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, Feuer EJ, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:10–30. - PubMed
-
- Malhotra V, Perry MC. Classical chemotherapy: mechanisms, toxicities and the therapeutic window. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2:S2–4. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Igney FH, Krammer PH. Death and anti-death: tumor resistance to apoptosis. Nature Rev Cancer. 2002;2:277–288. - PubMed
-
- Zornig M, Hueber AO, Baum W, Evan G. Apoptosis regulators and their role in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1551:F1–F37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

