Inhibition of Schistosoma mansoni thioredoxin-glutathione reductase by auranofin: structural and kinetic aspects
- PMID: 19710012
- PMCID: PMC2781444
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.020701
Inhibition of Schistosoma mansoni thioredoxin-glutathione reductase by auranofin: structural and kinetic aspects
Abstract
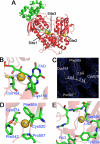
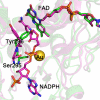
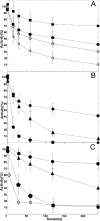
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease affecting over 200 million people currently treated with one drug, praziquantel. A possible drug target is the seleno-protein thioredoxin-glutathione reductase (TGR), a key enzyme in the pathway of the parasite for detoxification of reactive oxygen species. The enzyme is a unique fusion of a glutaredoxin domain with a thioredoxin reductase domain, which contains a selenocysteine (Sec) as the penultimate amino acid. Auranofin (AF), a gold-containing compound already in clinical use as an anti-arthritic drug, has been shown to inhibit TGR and to substantially reduce worm burden in mice. Using x-ray crystallography we solved (at 2.5 A resolution) the structure of wild type TGR incubated with AF. The electron density maps show that the actual inhibitor is gold, released from AF. Gold is bound at three different sites not directly involving the C-terminal Sec residue; however, because the C terminus in the electron density maps is disordered, we cannot exclude the possibility that gold may also bind to Sec. To investigate the possible role of Sec in the inactivation kinetics, we tested the effect of AF on a model enzyme of the same superfamily, i.e. the naturally Sec-lacking glutathione reductase, and on truncated TGR. We demonstrate that the role of selenium in the onset of inhibition by AF is catalytic and can be mimicked by an external source of selenium (benzeneselenol). Therefore, we propose that Sec mediates the transfer of gold from its ligands in AF to the redox-active Cys couples of TGR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thioredoxin glutathione reductase as a novel drug target: evidence from Schistosoma japonicum.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031456. Epub 2012 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384025 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the catalytic cycle of Schistosoma mansoni thioredoxin glutathione reductase by X-ray crystallography.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 15;285(42):32557-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.141960. Epub 2010 Jul 21. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20659890 Free PMC article.
-
Platyhelminth mitochondrial and cytosolic redox homeostasis is controlled by a single thioredoxin glutathione reductase and dependent on selenium and glutathione.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 27;283(26):17898-907. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710609200. Epub 2008 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18408002 Free PMC article.
-
Macromolecular bases of antischistosomal therapy.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(16):2012-28. doi: 10.2174/156802611796575939. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21619508 Review.
-
Targeting thioredoxin glutathione reductase as a potential antischistosomal drug target.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2018 Oct;225:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 30291946 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical and structural characterizations of thioredoxin reductase selenoproteins of the parasitic filarial nematodes Brugia malayi and Onchocerca volvulus.Redox Biol. 2022 May;51:102278. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102278. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 35276442 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of male and female Schistosoma mekongi adult worms.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Sep 10;11(1):504. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3086-z. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 30201055 Free PMC article.
-
New drug target in protozoan parasites: the role of thioredoxin reductase.Front Microbiol. 2015 Sep 30;6:975. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00975. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26483758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional utility of gold complexes with phosphorus donor ligands in biological systems.Coord Chem Rev. 2025 Jan 1;522:216208. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2024.216208. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Coord Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 39552640
-
A high-throughput drug screen for Entamoeba histolytica identifies a new lead and target.Nat Med. 2012 Jun;18(6):956-60. doi: 10.1038/nm.2758. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22610278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hotez P. J., Molyneux D. H., Fenwick A., Kumaresan J., Sachs S. E., Sachs J. D., Savioli L. (2007) N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 1018–1027 - PubMed
-
- Doenhoff M. J., Kusel J. R., Coles G. C., Cioli D. (2002) Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 96, 465–469 - PubMed
-
- Angelucci F., Basso A., Bellelli A., Brunori M., Pica-Mattoccia L., Valle C. (2007) Parasitology 134, 1215–1221 - PubMed
-
- Cioli D., Valle C., Angelucci F., Miele A. E. (2008) Trends Parasitol. 24, 379–382 - PubMed
-
- Salinas G., Selkirk M. E., Chalar C., Maizels R. M., Fernández C. (2004) Trends Parasitol. 20, 340–346 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

