Cortical inhibitory cell types differentially form intralaminar and interlaminar subnetworks with excitatory neurons
- PMID: 19710306
- PMCID: PMC6665698
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2219-09.2009
Cortical inhibitory cell types differentially form intralaminar and interlaminar subnetworks with excitatory neurons
Abstract
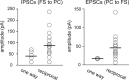
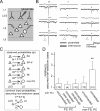
The neocortical circuit is composed of excitatory principal neurons and inhibitory interneurons. Recent advances have established that multiple subnetworks of synaptically coupled excitatory neurons provide distinct pathways for information flow through the cortical circuit. Here we have investigated how inhibitory interneurons are incorporated into these excitatory subnetworks in the rat frontal cortex. In layer 5 (L5), the probability of reciprocal synaptic connections between pyramidal cells and fast-spiking (FS) interneurons was significantly higher than the probability of reciprocal connections between pyramidal cells and non-FS interneurons. Further, the amplitude of synaptic currents in reciprocally connected FS/pyramidal cell pairs was larger than that in pairs connected only in one direction. To examine interlaminar connection specificity, we stimulated layer 2/3 (L2/3) pyramidal cells, using focal glutamate puff stimulation, and recorded evoked EPSCs in L5 cells. Stimulation of L2/3 cells evoked EPSCs in L5 non-FS cells more frequently than in L5 FS cells. Dual recordings from L5 interneurons and neighboring pyramidal cells revealed that connected non-FS/pyramidal cell pairs were more likely to share excitatory inputs from L2/3 cells than were unconnected cell pairs. On the other hand, the connectivity between L5 FS and pyramidal cell pairs did not affect the common input probability from L2/3. Our results suggest that L5 inhibitory interneurons form distinct intralaminar and interlaminar subnetworks with pyramidal cells, depending on inhibitory cell types.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional properties and short-term dynamics of unidirectional and reciprocal synaptic connections between layer 2/3 pyramidal cells and fast-spiking interneurons in juvenile rat prefrontal cortex.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Oct;38(7):2988-98. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12294. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23834038 Free PMC article.
-
Cell diversity and connection specificity between callosal projection neurons in the frontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 9;31(10):3862-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5795-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21389241 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-scale specificity of cortical networks depends on inhibitory cell type and connectivity.Nat Neurosci. 2005 Nov;8(11):1552-9. doi: 10.1038/nn1565. Epub 2005 Oct 9. Nat Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16222228
-
Control of excitatory hierarchical circuits by parvalbumin-FS basket cells in layer 5 of the frontal cortex: insights for cortical oscillations.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Jun 1;121(6):2222-2236. doi: 10.1152/jn.00778.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 17. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30995139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local connections of excitatory neurons in motor-associated cortical areas of the rat.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 May 28;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00075. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23754982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic Conductance Estimates of the Connection Between Local Inhibitor Interneurons and Pyramidal Neurons in Layer 2/3 of a Cortical Column.Cereb Cortex. 2015 Nov;25(11):4415-29. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv039. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Cereb Cortex. 2015. PMID: 25761638 Free PMC article.
-
Sparse distributed representation of odors in a large-scale olfactory bulb circuit.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(3):e1003014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003014. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23555237 Free PMC article.
-
Basket cell dichotomy in microcircuit function.J Physiol. 2012 Feb 15;590(4):683-94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.223669. Epub 2011 Dec 23. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22199164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superficial Layers Suppress the Deep Layers to Fine-tune Cortical Coding.J Neurosci. 2019 Mar 13;39(11):2052-2064. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1459-18.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30651326 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional mapping of microcircuit correlation structure.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 Oct 10;7:151. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00151. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 24133414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dantzker JL, Callaway EM. Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:701–707. - PubMed
-
- de Lima AD, Morrison JH. Ultrastructural analysis of somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons and synapses in the temporal and occipital cortex of the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1989;283:212–227. - PubMed
-
- Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1:1–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
