Beta-amyloid monomers are neuroprotective
- PMID: 19710311
- PMCID: PMC6665714
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1736-09.2009
Beta-amyloid monomers are neuroprotective
Abstract
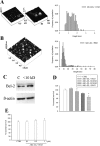
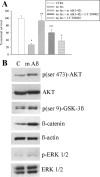
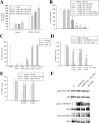
The 42-aa-long beta-amyloid protein--Abeta(1-42)--is thought to play a central role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) (Walsh and Selkoe, 2007). Data from AD brain (Shankar et al., 2008), transgenic APP (amyloid precursor protein)-overexpressing mice (Lesné et al., 2006), and neuronal cultures treated with synthetic Abeta peptides (Lambert et al., 1998) indicate that self-association of Abeta(1-42) monomers into soluble oligomers is required for neurotoxicity. The function of monomeric Abeta(1-42) is unknown. The evidence that Abeta(1-42) is present in the brain and CSF of normal individuals suggests that the peptide is physiologically active (Shoji, 2002). Here we show that synthetic Abeta(1-42) monomers support the survival of developing neurons under conditions of trophic deprivation and protect mature neurons against excitotoxic death, a process that contributes to the overall neurodegeneration associated with AD. The neuroprotective action of Abeta(1-42) monomers was mediated by the activation of the PI-3-K (phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase) pathway, and involved the stimulation of IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1) receptors and/or other receptors of the insulin superfamily. Interestingly, monomers of Abeta(1-42) carrying the Arctic mutation (E22G) associated with familiar AD (Nilsberth et al., 2001) were not neuroprotective. We suggest that pathological aggregation of Abeta(1-42) may also cause neurodegeneration by depriving neurons of the protective activity of Abeta(1-42) monomers. This "loss-of-function" hypothesis of neuronal death should be taken into consideration when designing therapies aimed at reducing Abeta burden.
Figures
References
-
- Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Avruch J. Insulin signal transduction through protein kinase cascades. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;182:31–48. - PubMed
-
- Copani A, Koh JY, Cotman CW. Beta-amyloid increases neuronal susceptibility to injury by glucose deprivation. Neuroreport. 1991;2:763–765. - PubMed
-
- Copani A, Condorelli F, Caruso A, Vancheri C, Sala A, Giuffrida Stella AM, Canonico PL, Nicoletti F, Sortino MA. Mitotic signaling by beta-amyloid causes neuronal death. FASEB J. 1999;13:2225–2234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
