Astrocytic dysfunction in epileptogenesis: consequence of altered potassium and glutamate homeostasis?
- PMID: 19710312
- PMCID: PMC2875068
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2323-09.2009
Astrocytic dysfunction in epileptogenesis: consequence of altered potassium and glutamate homeostasis?
Abstract
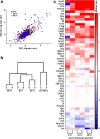
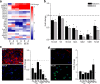
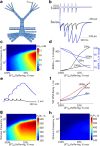
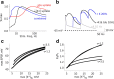
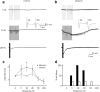
Focal epilepsy often develops following traumatic, ischemic, or infectious brain injury. While the electrical activity of the epileptic brain is well characterized, the mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis are poorly understood. We have recently shown that in the rat neocortex, long-lasting breakdown of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) or direct exposure of the neocortex to serum-derived albumin leads to rapid upregulation of the astrocytic marker GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein), followed by delayed (within 4-7 d) development of an epileptic focus. We investigated the role of astrocytes in epileptogenesis in the BBB-breakdown and albumin models of epileptogenesis. We found similar, robust changes in astrocytic gene expression in the neocortex within hours following treatment with deoxycholic acid (BBB breakdown) or albumin. These changes predict reduced clearance capacity for both extracellular glutamate and potassium. Electrophysiological recordings in vitro confirmed the reduced clearance of activity-dependent accumulation of both potassium and glutamate 24 h following exposure to albumin. We used a NEURON model to simulate the consequences of reduced astrocytic uptake of potassium and glutamate on EPSPs. The model predicted that the accumulation of glutamate is associated with frequency-dependent (>100 Hz) decreased facilitation of EPSPs, while potassium accumulation leads to frequency-dependent (10-50 Hz) and NMDA-dependent synaptic facilitation. In vitro electrophysiological recordings during epileptogenesis confirmed frequency-dependent synaptic facilitation leading to seizure-like activity. Our data indicate a transcription-mediated astrocytic transformation early during epileptogenesis. We suggest that the resulting reduction in the clearance of extracellular potassium underlies frequency-dependent neuronal hyperexcitability and network synchronization.
Figures


References
-
- Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Araque A, Carmignoto G, Haydon PG. Dynamic signaling between astrocytes and neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 2001;63:795–813. - PubMed
-
- Arnth-Jensen N, Jabaudon D, Scanziani M. Cooperation between independent hippocampal synapses is controlled by glutamate uptake. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:325–331. - PubMed
-
- Barres BA, Chun LL, Corey DP. Ion channels in vertebrate glia. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:441–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
