DNA-based MRI probes for specific detection of chronic exposure to amphetamine in living brains
- PMID: 19710318
- PMCID: PMC2746375
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2167-09.2009
DNA-based MRI probes for specific detection of chronic exposure to amphetamine in living brains
Abstract
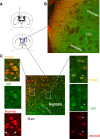
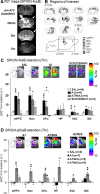
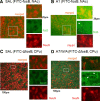
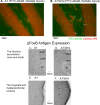
We designed phosphorothioate-modified DNA probes linked to superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) for in vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of fosB and Delta fosB mRNA after amphetamine (AMPH) exposure in mice. Specificity of both the fosB and Delta fosB probes was verified by in vitro reverse transcriptase-PCR amplification to a single fragment of total cDNA obtained from acutely AMPH-exposed mouse brains. We confirmed time-dependent uptake and retention profiles of both probes in neurons of GAD67-green fluorescent protein knock-in mice. MRI signal of SPION-labeled fosB probe delivered via intracerebroventricular route was elevated in both acutely and chronically AMPH-exposed mice; the signal was suppressed by dopaminergic receptor antagonist pretreatment. SPION-labeled Delta fosB probe signal elevation occurred only in chronically AMPH-exposed mice. The in vivo target specificity of these probes permits reliable MRI visualization of AMPH-induced differential elevations of fosB and Delta fosB mRNA in living brains.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MRI reveals differential effects of amphetamine exposure on neuroglia in vivo.FASEB J. 2013 Feb;27(2):712-24. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-220061. Epub 2012 Nov 12. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23150521 Free PMC article.
-
MR contrast probes that trace gene transcripts for cerebral ischemia in live animals.FASEB J. 2007 Sep;21(11):3004-15. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-8203com. Epub 2007 May 3. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17478745 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of fosB and DeltafosB mRNA expression: in vivo and in vitro studies.Brain Res. 2007 Apr 27;1143:22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.069. Epub 2007 Jan 27. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17324382 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of amphetamine action revealed in mice lacking the dopamine transporter.J Neurosci. 1998 Mar 15;18(6):1979-86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-06-01979.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9482784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription MRI: a new view of the living brain.Neuroscientist. 2008 Oct;14(5):503-20. doi: 10.1177/1073858407309746. Epub 2007 Nov 16. Neuroscientist. 2008. PMID: 18024855 Review.
Cited by
-
Big Potential from Small Agents: Nanoparticles for Imaging-Based Companion Diagnostics.ACS Nano. 2018 Mar 27;12(3):2106-2121. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07252. Epub 2018 Mar 1. ACS Nano. 2018. PMID: 29462554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRI reveals differential effects of amphetamine exposure on neuroglia in vivo.FASEB J. 2013 Feb;27(2):712-24. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-220061. Epub 2012 Nov 12. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23150521 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Intrathecal Nanoparticle Delivery: Targeting the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier for Enhanced CNS Drug Delivery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;17(8):1070. doi: 10.3390/ph17081070. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is there a path beyond BOLD? Molecular imaging of brain function.Neuroimage. 2012 Aug 15;62(2):1208-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.02.076. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22406355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics of amphetamine-induced sensitization: HDAC5 expression and microRNA in neural remodeling.J Biomed Sci. 2016 Dec 8;23(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0294-8. J Biomed Sci. 2016. PMID: 27931227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boxerman JL, Hamberg LM, Rosen BR, Weisskoff RM. MR contrast due to intravascular magnetic susceptibility perturbations. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:555–566. - PubMed
-
- Brown JR, Ye H, Bronson RT, Dikkes P, Greenberg ME. A defect in nurturing in mice lacking the immediate early gene fosB. Cell. 1996;86:297–309. - PubMed
-
- Conversi D, Bonito-Oliva A, Orsini C, Colelli V, Cabib S. DeltaFosB accumulation in ventro-medial caudate underlies the induction but not the expression of behavioral sensitization by both repeated amphetamine and stress. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:191–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21DA024235/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA026108/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS057556/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 EB008134/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS045776/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA026108/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA020796/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS057556/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB002066/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01EB002066/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS045776/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045845/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA020796/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R03EB008134/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS045845/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA024235/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
