Nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor activation attenuates antinociception induced by mixed nociceptin/orphanin FQ/mu-opioid receptor agonists
- PMID: 19713488
- PMCID: PMC2784721
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.156711
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor activation attenuates antinociception induced by mixed nociceptin/orphanin FQ/mu-opioid receptor agonists
Abstract
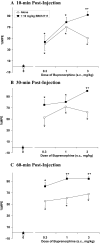
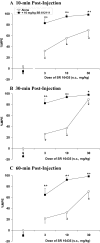
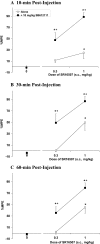
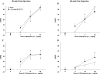
Activation of brain nociceptin/orphanin FQ (NOP) receptors leads to attenuation of mu-opioid receptor (MOP receptor)-mediated antinociception. Buprenorphine, a high-affinity partial MOP receptor agonist also binds to NOP receptors with 80 nM affinity. The buprenorphine-induced inverted U-shaped dose-response curve for antinociception may be due to NOP receptor activation, given that, in the presence of the NOP receptor antagonist, 1-[(3R,4R)-1-cyclooctylmethyl-3-hydroxymethyl-4-piperidyl]-3-ethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one (J113397), or in NOP receptor knockout mice, buprenorphine has a steeper dose-response curve and acts as a full agonist. To further explore the involvement of the direct activation of NOP receptors by buprenorphine and other compounds that activate both NOP and MOP receptors, the antinociceptive effects of 1-(1-(2,3,3alpha,4,5,6-hexahydro-1H-phenalen-1-yl)piperidin-4-yl)-indolin-2-one. (SR16435), 3-ethyl-1-(1-(4-isopropylcyclohexyl)piperidin-4-yl)-indolin-2-one (SR16507), buprenorphine, pentazocine, and morphine, compounds with varying levels of MOP and NOP receptor affinity and efficacy, were assessed in mice using the tail-flick assay. The ability of the selective NOP receptor antagonist (-)-cis-1-methyl-7-[[4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]methyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-benzocyclohepten-5-ol (SB-612111) to potentiate antinociception induced by the above compounds was examined to investigate whether activation of NOP receptors leads to attenuation of MOP receptor-mediated antinociception. SB-612111 potentiated antinociception induced by buprenorphine and the other mixed NOP/MOP receptor agonists SR16435 and SR16507. However, SB-612111 had no effect on pentazocine or morphine antinociception, two compounds with no NOP receptor-binding affinity. These results further support the hypothesis that activation of NOP receptors can lead to attenuation of MOP receptor-mediated antinociception elicited by mixed NOP/MOP receptor compounds such as buprenorphine, SR16435, and SR16507 and that, although buprenorphine has low efficacy in vitro, it has significant NOP receptor agonist activity in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of spinally administered bifunctional nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide receptor/μ-opioid receptor ligands in mouse models of neuropathic and inflammatory pain.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Jul;346(1):11-22. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.203984. Epub 2013 May 7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23652222 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of μ-opioid receptors and nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide receptors in buprenorphine-induced physiological responses in primates.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Oct;343(1):72-81. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.194308. Epub 2012 Jun 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22743574 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of nociceptin/orphanin FQ (NOP) receptor agonists in acute versus chronic pain: studies with bifunctional NOP/μ receptor agonists in the sciatic nerve ligation chronic pain model in mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Nov;339(2):687-93. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.184663. Epub 2011 Aug 22. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21859931 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor agonists as analgesics without abuse liability.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Feb 20;4(2):214-24. doi: 10.1021/cn300124f. Epub 2012 Nov 6. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23421672 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural determinants of opioid and NOP receptor activity in derivatives of buprenorphine.J Med Chem. 2011 Oct 13;54(19):6531-7. doi: 10.1021/jm2003238. Epub 2011 Sep 7. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21866885 Free PMC article.
-
Selective κ receptor partial agonist HS666 produces potent antinociception without inducing aversion after i.c.v. administration in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Aug;174(15):2444-2456. doi: 10.1111/bph.13854. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28494108 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Treatments for Neuropathic Pain.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2015 Dec;19(12):56. doi: 10.1007/s11916-015-0530-z. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2015. PMID: 26530058 Review.
-
A bifunctional nociceptin and mu opioid receptor agonist is analgesic without opioid side effects in nonhuman primates.Sci Transl Med. 2018 Aug 29;10(456):eaar3483. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aar3483. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30158150 Free PMC article.
-
BU10038 as a safe opioid analgesic with fewer side-effects after systemic and intrathecal administration in primates.Br J Anaesth. 2019 Jun;122(6):e146-e156. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.10.065. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Br J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 30916003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng Y, Prusoff WH. (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 percent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108 - PubMed
-
- Ciccocioppo R, Economidou D, Fedeli A, Angeletti S, Weiss F, Heilig M, Massi M. (2004) Attenuation of ethanol self-administration and of conditioned reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behaviour by the antiopioid peptide nociceptin/orphanin FQ in alcohol-preferring rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 172:170–178 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

