The co-regulation of emotions between mothers and their children with autism
- PMID: 19714458
- PMCID: PMC2810360
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-009-0861-x
The co-regulation of emotions between mothers and their children with autism
Abstract
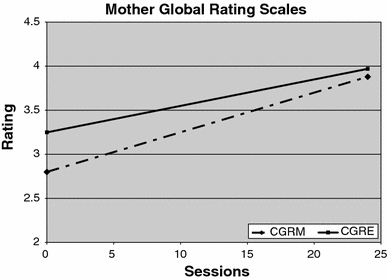
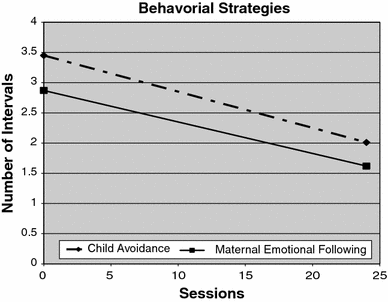
Thirty-four toddlers with autism and their mothers participated in an early intervention targeting joint engagement. Across the 24 intervention sessions, any significant distress episode in the child was coded for emotion regulation outcomes including child negativity, child emotion self-regulation, and mother emotion co-regulation. Results revealed that emotion regulation strategies by both mother and child were employed during distress episodes. An effect of intervention was found such that children decreased their expression of negativity across the intervention and mothers increased their emotional and motivational scaffolding. The results of this study indicate a positive effect of an intervention targeting joint engagement on emotion co-regulation outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Abidin RR. Parenting stress index manual. Charlottesville, VA: Pediatric Psychology Press; 1983.
-
- Adamson L, McArthur D, Markoc Y, Dubar B, Bakeman R. Autism and joint attention: Young children’s responses to maternal bids. Applied Developmental Psychology. 2001;22:439–453. doi: 10.1016/S0193-3973(01)00089-2. - DOI