Novel evidence-based systemic lupus erythematosus responder index
- PMID: 19714615
- PMCID: PMC2748175
- DOI: 10.1002/art.24698
Novel evidence-based systemic lupus erythematosus responder index
Abstract
Objective: To describe a new systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) responder index (SRI) based on a belimumab phase II SLE trial and demonstrate its potential utility in SLE clinical trials.
Methods: Data from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 449 patients of 3 doses of belimumab (1, 4, 10 mg/kg) or placebo plus standard of care therapy (SOC) over a 56-week period were analyzed. The Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus: National Assessment (SELENA) version of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) and British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) SLE disease activity instruments, the Short Form 36 health survey, and biomarker analyses were used to create a novel SRI. Response to treatment in a subset of 321 serologically active SLE patients (antinuclear antibodies >/=1:80 and/or anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies >/=30 IU/ml) at baseline was retrospectively evaluated using the SRI.
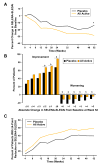
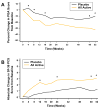
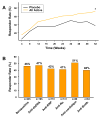
Results: SRI response is defined as 1) a >/=4-point reduction in SELENA-SLEDAI score, 2) no new BILAG A or no more than 1 new BILAG B domain score, and 3) no deterioration from baseline in the physician's global assessment by >/=0.3 points. In serologically active patients, the addition of belimumab to SOC resulted in a response in 46% of patients at week 52 compared with 29% of the placebo patients (P = 0.006). SRI responses were independent of baseline autoantibody subtype.
Conclusion: This evidence-based evaluation of a large randomized, placebo-controlled trial in SLE resulted in the ability to define a robust responder index based on improvement in disease activity without worsening the overall condition or the development of significant disease activity in new organ systems.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00071487.
Figures

Comment in
-
Global versus organ-specific outcome measures in systemic lupus erythematosus: comment on the articles by Furie et al, Nikpour et al, Wallace et al, Burgos et al, and Ramos-Casals et al.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010 Apr;62(4):580-1; author replies 581-2. doi: 10.1002/acr.20053. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010. PMID: 20391517 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(9):929–39. - PubMed
-
- ACR Ad Hoc Committee. Guidelines for Referral and Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Adults. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(9):1785–96. - PubMed
-
- Strand V. Lessons learned from clinical trials in SLE. Autoimmun Rev. 2007;6(4):209–14. - PubMed
-
- FDA. Guidance for Industry Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Developing Drugs for Treatment. 2005. [Last accessed on 8/12/2008]. http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/6496dft.pdf.
-
- Bertsias G, Gordon C, Boumpas D. Clinical trials in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): lessons from the past as we proceed to the future - the EULAR recommendations for the management of SLE and the use of end-points in clinical trials. Lupus. 2008;17(5):437–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

