Active-site determinants of substrate recognition by the metalloproteinases TACE and ADAM10
- PMID: 19715556
- PMCID: PMC2774824
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20090549
Active-site determinants of substrate recognition by the metalloproteinases TACE and ADAM10
Abstract
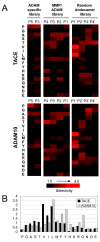
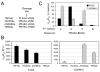
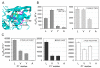
The metalloproteinases TACE [tumour necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme; also known as ADAM17 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17)] and ADAM10 are the primary enzymes responsible for catalysing release of membrane-anchored proteins from the cell surface in metazoan organisms. Although the repertoire of protein substrates for these two proteases is partially overlapping, each one appears to target a subset of unique proteins in vivo. The mechanisms by which the two proteases achieve specificity for particular substrates are not completely understood. We have used peptide libraries to define the cleavage site selectivity of TACE and ADAM10. The two proteases have distinct primary sequence requirements at multiple positions surrounding the cleavage site in their substrates, which allowed us to generate peptide substrates that are highly specific for each of these proteases. The major difference between the two protease specificities maps to the P1' position (immediately downstream of the cleavage site) of the substrate. At this position, TACE is selective for smaller aliphatic residues, whereas ADAM10 can accommodate aromatic amino acids. Using mutagenesis we identified three residues in the S1' pockets of these enzymes that dramatically influence specificity for both peptide and protein substrates. Our results suggest that substrate selectivity of TACE and ADAM10 can be at least partly rationalized by specific features of their active sites.
Figures

References
-
- Becherer JD, Blobel CP. Biochemical properties and functions of membrane-anchored metalloprotease-disintegrin proteins (ADAMs) Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2003;54:101–123. - PubMed
-
- Black RA, White JM. ADAMs: focus on the protease domain. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1998;10:654–659. - PubMed
-
- Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ, Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Wolfson MF, Castner BJ, Stocking KL, Reddy P, Srinivasan S, Nelson N, Boiani N, Schooley KA, Gerhart M, Davis R, Fitzner JN, Johnson RS, Paxton RJ, March CJ, Cerretti DP. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-α from cells. Nature. 1997;385:729–733. - PubMed
-
- Moss ML, Jin SL, Milla ME, Bickett DM, Burkhart W, Carter HL, Chen WJ, Clay WC, Didsbury JR, Hassler D, Hoffman CR, Kost TA, Lambert MH, Leesnitzer MA, McCauley P, McGeehan G, Mitchell J, Moyer M, Pahel G, Rocque W, Overton LK, Schoenen F, Seaton T, Su JL, Becherer JD, et al. Cloning of a disintegrin metalloproteinase that processes precursor tumour-necrosis factor-α. Nature. 1997;385:733–736. - PubMed
-
- Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Reddy P, Stocking KL, Sunnarborg SW, Lee DC, Russell WE, Castner BJ, Johnson RS, Fitzner JN, Boyce RW, Nelson N, Kozlosky CJ, Wolfson MF, Rauch CT, Cerretti DP, Paxton RJ, March CJ, Black RA. An essential role for ectodomain shedding in mammalian development. Science. 1998;282:1281–1284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

