Reproducibility of quantitative RT-PCR array in miRNA expression profiling and comparison with microarray analysis
- PMID: 19715577
- PMCID: PMC2753550
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-407
Reproducibility of quantitative RT-PCR array in miRNA expression profiling and comparison with microarray analysis
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have critical functions in various biological processes. MiRNA profiling is an important tool for the identification of differentially expressed miRNAs in normal cellular and disease processes. A technical challenge remains for high-throughput miRNA expression analysis as the number of miRNAs continues to increase with in silico prediction and experimental verification. Our study critically evaluated the performance of a novel miRNA expression profiling approach, quantitative RT-PCR array (qPCR-array), compared to miRNA detection with oligonucleotide microchip (microarray).
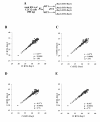
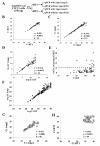
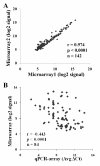
Results: High reproducibility with qPCR-array was demonstrated by comparing replicate results from the same RNA sample. Pre-amplification of the miRNA cDNA improved sensitivity of the qPCR-array and increased the number of detectable miRNAs. Furthermore, the relative expression levels of miRNAs were maintained after pre-amplification. When the performance of qPCR-array and microarrays were compared using different aliquots of the same RNA, a low correlation between the two methods (r=-0.443) indicated considerable variability between the two assay platforms. Higher variation between replicates was observed in miRNAs with low expression in both assays. Finally, a higher false positive rate of differential miRNA expression was observed using the microarray compared to the qPCR-array.
Conclusion: Our studies demonstrated high reproducibility of TaqMan qPCR-array. Comparison between different reverse transcription reactions and qPCR-arrays performed on different days indicated that reverse transcription reactions did not introduce significant variation in the results. The use of cDNA pre-amplification increased the sensitivity of miRNA detection. Although there was variability associated with pre-amplification in low abundance miRNAs, the latter did not involve any systemic bias in the estimation of miRNA expression. Comparison between microarray and qPCR-array indicated superior sensitivity and specificity of qPCR-array.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

