Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and postmenopausal breast cancer risk: a nested case control study in the Cancer Prevention Study-II Nutrition Cohort
- PMID: 19715600
- PMCID: PMC2750126
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2356
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and postmenopausal breast cancer risk: a nested case control study in the Cancer Prevention Study-II Nutrition Cohort
Abstract
Introduction: Vitamin D status measured during adulthood has been inversely associated with breast cancer risk in some, but not all, studies. Vitamin D has been hypothesized to prevent breast cancer through genomic and non-genomic actions in cell-cycle regulation.
Methods: A subset (n = 21,965) of female participants from the prospective Cancer Prevention Study-II (CPS-II) Nutrition Cohort provided a blood sample from 1998-2001 and were followed through 2005. We measured serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in 516 verified incident cases and 516 controls, matched on birth date (+/- 6 months), date of blood draw (+/- 6 months) and race. Information on medical history, risk factors and lifestyle was available from repeated questionnaires. We computed multi-variable odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for the association between 25(OH)D quintile and breast cancer risk using unconditional logistic regression, controlling for matching factors and additional confounders.
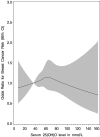
Results: We observed no association between 25(OH)D and breast cancer (OR = 1.09, 95% CI 0.70-1.68, P = 0.60) for the top vs bottom quintile. Using a priori cut-points, the OR was 0.86 (95% CI 0.59-1.26), for > or =75 vs <50 nmol/L. Results were not different when the first two years of follow-up were excluded, or in analyses stratified by season, latitude, BMI, postmenopausal hormone use, or by tumor grade or estrogen receptor status.
Conclusions: These results do not support an association between adulthood serum 25(OH)D and postmenopausal breast cancer. We cannot rule out an association with 25(OH)D status earlier in life.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2009. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2009.
-
- World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research Food, Nutrition, and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective. Washington DC AICR. 2007 doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(90)90058-R. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

