Overexpression of wild-type murine tau results in progressive tauopathy and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 19717642
- PMCID: PMC2751556
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090462
Overexpression of wild-type murine tau results in progressive tauopathy and neurodegeneration
Abstract
Here, we describe the generation and characterization of a novel tau transgenic mouse model (mTau) that overexpresses wild-type murine tau protein by twofold compared with endogenous levels. Transgenic tau expression was driven by a BAC transgene containing the entire wild-type mouse tau locus, including the endogenous promoter and the regulatory elements associated with the tau gene. The mTau model therefore differs from other tau models in that regulation of the genomic mouse transgene mimics that of the endogenous gene, including normal exon splicing regulation. Biochemical data from the mTau mice demonstrated that modest elevation of mouse tau leads to tau hyperphosphorylation at multiple pathologically relevant epitopes and accumulation of sarkosyl-insoluble tau. The mTau mice show a progressive increase in hyperphosphorylated tau pathology with age up to 15 to 18 months, which is accompanied by gliosis and vacuolization. In contrast, older mice show a decrease in tau pathology levels, which may represent hippocampal neuronal loss occurring in this wild-type model. Collectively, these results describe a novel model of tauopathy that develops pathological changes reminiscent of early stage Alzheimer's disease and other related neurodegenerative diseases, achieved without overexpression of a mutant human tau transgene. This model will provide an important tool for understanding the early events leading to the development of tau pathology and a model for analysis of potential therapeutic targets for sporadic tauopathies.
Figures
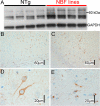

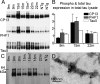
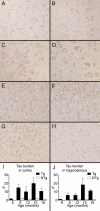

References
-
- Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Jakes R, Rutherford D, Crowther RA. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 1989;3:519–526. - PubMed
-
- Andreadis A, Brown WM, Kosi KS. Structure and novel exons of the human tau gene. Biochemistry. 1992;31:10626–10633. - PubMed
-
- Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Pertersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaff E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebrand M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski J, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd PR, Hayward N, Kwok JB, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann D, Lynch T, Heutink P. Association of missense and 5′-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature. 1998;393:702–705. - PubMed
-
- Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E, Nemens E, Garruto RM, Anderson L, Andreadis A, Wiederholt WC, Raskind M, Schellenberg GD. is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol. 1998;43:815–825. - PubMed
-
- Eriksen JL, Zehr C, Lewis J. Biologic models of neurodegenerative disorders. Duyckaerts C, Litvan I, editors. New York,: Elsevier,; 2008:pp. 173–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

