The influence that electronic prescribing has on medication errors and preventable adverse drug events: an interrupted time-series study
- PMID: 19717798
- PMCID: PMC3002127
- DOI: 10.1197/jamia.M3099
The influence that electronic prescribing has on medication errors and preventable adverse drug events: an interrupted time-series study
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluated the effect of a Computerized Physician Order Entry system with basic Clinical Decision Support (CPOE/CDSS) on the incidence of medication errors (MEs) and preventable adverse drug events (pADEs).
Design: Interrupted time-series design.
Measurements: The primary outcome measurements comprised the percentage of medication orders with one or more MEs and the percentage of patients with one or more pADEs.
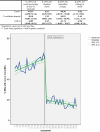
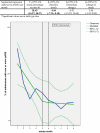
Results: Pre-implementation, the mean percentage of medication orders containing at least one ME was 55%, whereas this became 17% post-implementation. The introduction of CPOE/CDSS has led to a significant immediate absolute reduction of 40.3% (95% CI: -45.13%; -35.48%) in medication orders with one or more errors. Pre-implementation, the mean percentage of admitted patients experiencing at least one pADE was 15.5%, as opposed to 7.3% post-implementation. However, this decrease could not be attributed to the introduction of CPOE/CDSS: taking into consideration the interrupted time-series design, the immediate change was not significant (-0.42%, 95% CI: -15.52%; 14.68%) because of the observed underlying negative trend during the pre-CPOE period of -4.04% [95% CI: -7.70%; -0.38%] per month.
Conclusions: This study has shown that CPOE/CDSS reduces the incidence of medication errors. However, a direct effect on actual patient harm (pADEs) was not demonstrated.
Figures



References
-
- To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Health SystemWashington, DC: National Academies Press; 1999. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhry B, Wang J, Wu S, et al. Systematic review: Impact of health information technology on quality, efficiency, and costs of medical care Ann Intern Med 2006;144(10):742-752. - PubMed
-
- Bates DW, Leape LL, Cullen DJ, et al. Effect of computerized physician order entry and a team intervention on prevention of serious medication errors J Am Med Assoc 1998;280(15):1311-1316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

