Serotonin decreases alveolar epithelial fluid transport via a direct inhibition of the epithelial sodium channel
- PMID: 19717814
- PMCID: PMC2911574
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0472OC
Serotonin decreases alveolar epithelial fluid transport via a direct inhibition of the epithelial sodium channel
Abstract
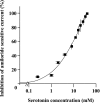
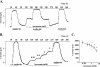
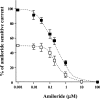
Hypoxia and epithelial stretch that are commonly observed in patients with acute lung injury have been shown to promote the release of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) in vitro. However, whether 5-HT contributes to the decrease of alveolar epithelial fluid transport, which is a hallmark of lung injury, is unknown. Thus, we investigated the effect of 5-HT on ion and fluid transport across the alveolar epithelium. 5-HT caused a dose-dependent inhibition of the amiloride-sensitive current across primary rat and human alveolar epithelial type II cell monolayers, but did not affect Na(+)/K(+) ATPase function. Furthermore, we found that the 5-HT induced inhibition of ion transport across the lung epithelium was receptor independent, as it was not prevented by the blockade of 5-HT2R (5-HT receptor 2), 5-HT3R (5-HT receptor 3), or by pretreatment with an intracellular calcium-chelating agent, BAPTA-AM (1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid tetra(acetoxymethyl) ester). In addition, the stimulation of 5-HT1R (5-HT receptor 1), 5-HT2R (5-HT receptor 2), 5-HT4R (5-HT receptor 4), and 5-HT7R (5-HT receptor 7) failed to reproduce the 5-HT effect on amiloride-sensitive sodium transport. We ascertained that 5-HT directly inhibited the function of rat alphabetagamma epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), as determined by heterologous expression of rat ENaC in Xenopus oocytes that do not express endogenous ENaC nor 5-HT receptors (5-HTR). Exposure of mice to hypoxia for 1 hour induced a 30% increase of 5-HT secretion into the distal airways of mice. Finally, the intratracheal instillation of 5-HT inhibited the amiloride-sensitive fraction of alveolar fluid clearance in mice. Together, these results indicate that 5-HT inhibits the amiloride-sensitive fraction of the alveolar epithelial fluid transport via a direct interaction with ENaC, and thus can be an endogenous inhibitor of this ion channel.
Figures


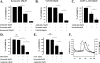
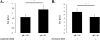
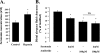
Similar articles
-
Dexamethasone prevents transport inhibition by hypoxia in rat lung and alveolar epithelial cells by stimulating activity and expression of Na+-K+-ATPase and epithelial Na+ channels.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007 Nov;293(5):L1332-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00338.2006. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17873005
-
Hypoxia-induced inhibition of epithelial Na(+) channels in the lung. Role of Nedd4-2 and the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014 Mar;50(3):526-37. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0518OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24093724
-
Alpha(1)-antitrypsin inhibits epithelial Na+ transport in vitro and in vivo.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Sep;41(3):261-70. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0384OC. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19131639 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical and molecular properties of amiloride-inhibitable Na+ channels in alveolar epithelial cells.Am J Physiol. 1996 Jul;271(1 Pt 1):L1-22. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1996.271.1.L1. Am J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8760127 Review.
-
Amiloride-insensitive Na+ and fluid absorption in the mammalian distal lung.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Mar;294(3):L401-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00431.2007. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18162600 Review.
Cited by
-
Amiloride-sensitive sodium channels and pulmonary edema.Pulm Med. 2011;2011:830320. doi: 10.1155/2011/830320. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Pulm Med. 2011. PMID: 21637371 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and functional heterogeneity of the airway epithelium.Mucosal Immunol. 2021 Sep;14(5):978-990. doi: 10.1038/s41385-020-00370-7. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Mucosal Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33608655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroendocrine signaling via the serotonin transporter regulates clearance of apoptotic cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 11;289(15):10466-10475. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.482299. Epub 2014 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24570000 Free PMC article.
-
The role of stretch-activated ion channels in acute respiratory distress syndrome: finally a new target?Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;311(3):L639-52. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00458.2015. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27521425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathologic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Radiation-Induced Lung Injury in Nonhuman Primates.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Sep 1;111(1):249-259. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.03.058. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33848608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matthay MA, Robriquet L, Fang X. Alveolar epithelium: role in lung fluid balance and acute lung injury. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2005;2:206–213. - PubMed
-
- Matthay MA, Folkesson HG, Clerici C. Lung epithelial fluid transport and the resolution of pulmonary edema. Physiol Rev 2002;82:569–600. - PubMed
-
- Hummler E, Baker P, Gatzy J, Beerman F, Verdumo C, Schmidt A, Boucher R, Rossier BC. Early death due to defective neonatal lung liquid clearance in alpha-ENaC–deficient mice. Nat Genet 1996;12:325–328. - PubMed
-
- Planes C, Escoubet B, Blot-Chabaud M, Friedlander G, Farman N, Clerici C. Hypoxia downregulates expression and activity of epithelial sodium channels in rat alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1997;17:508–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

