Structural basis of high-fidelity DNA synthesis by yeast DNA polymerase delta
- PMID: 19718023
- PMCID: PMC3055789
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1663
Structural basis of high-fidelity DNA synthesis by yeast DNA polymerase delta
Abstract
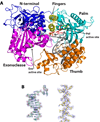
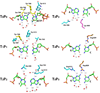
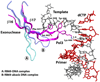
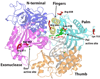
DNA polymerase delta (Pol delta) is a high-fidelity polymerase that has a central role in replication from yeast to humans. We present the crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of yeast Pol delta in ternary complex with a template primer and an incoming nucleotide. The structure, determined at 2.0-A resolution, catches the enzyme in the act of replication, revealing how the polymerase and exonuclease domains are juxtaposed relative to each other and how a correct nucleotide is selected and incorporated. The structure also reveals the 'sensing' interactions near the primer terminus, which signal a switch from the polymerizing to the editing mode. Taken together, the structure provides a chemical basis for the bulk of DNA synthesis in eukaryotic cells and a framework for understanding the effects of cancer-causing mutations in Pol delta.
Figures


References
-
- Garg P, Burgers PM. DNA polymerases that propagate the eukaryotic DNA replication fork. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;40:115–128. - PubMed
-
- Johnson A, O'Donnell M. Cellular DNA replicases: components and dynamics at the replication fork. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:283–315. - PubMed
-
- Hartwell LH. Sequential function of gene products relative to DNA synthesis in the yeast cell cycle. J Mol Biol. 1976;104:803–817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

