Intact rapid detection of fearful faces in the absence of the amygdala
- PMID: 19718036
- PMCID: PMC2756300
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2380
Intact rapid detection of fearful faces in the absence of the amygdala
Abstract
The amygdala is thought to process fear-related stimuli rapidly and nonconsciously. We found that an individual with complete bilateral amygdala lesions, who cannot recognize fear from faces, nonetheless showed normal rapid detection and nonconscious processing of those same fearful faces. We conclude that the amygdala is not essential for early stages of fear processing but, instead, modulates recognition and social judgment.
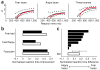
Figures
References
-
- Adolphs R, Tranel D, Damasio H, Damasio A. Nature. 1994;372:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Ohman A, Carlsson K, Lundqvist D, Ingvar M. Physiol Behav. 2007;92:180–185. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, He S. Curr Biol. 2006;16:2023–2029. - PubMed
-
- Pessoa L, Japee S, Sturman D, Ungerleider LG. Cereb Cortex. 2006;16:366–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

