Immunoglobulin V(H) chain gene analysis of peripheral blood IgM-producing B cells in patients with Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 19718396
- PMCID: PMC2730610
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.4.493
Immunoglobulin V(H) chain gene analysis of peripheral blood IgM-producing B cells in patients with Kawasaki disease
Erratum in
- Yonsei Med J. 2009 Oct 31;50(5):736. Park, In Ho [added]; Shin, Jun Soo [corrected to Shin, Jeon-Soo]
Abstract
Purpose: Kawasaki disease is a systemic vasculitis, and its etiology and pathogenesis are still not clear. Our study was undertaken to investigate the characteristics of the activation of B cells in the peripheral blood of Kawasaki disease (KD) patients and evidence of stimulation by superantigens.
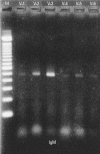
Materials and methods: Blood samples were obtained from three patients (2 males, 1 female) with KD, who were admitted to our Hospital, Seoul, Korea. The mean age was 1.2 years. Distribution of B cells was studied in the acute and subacute phases of KD patients. From the RNA of B cells, we obtained complementary DNA (cDNA) and performed polymerase chain reaction (PCR). To determine the oligoclonal expansion of immunoglobulin M (IgM) V(H) family, we cloned and sequenced the PCR products from each group and analyzed DNA.
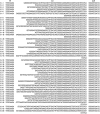
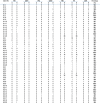
Results: In the peripheral blood of acute phase patients, T cells were significantly decreased (p < 0.05), whereas B cells were significantly increased (p < 0.05). When the first PCR was done on the B cell chains, V(H)1 to V(H)6 were all found to be expressed. The number of micro gene clones obtained from 3 patients was 312, and they belonged to V(H)3, V(H)4 and V(H)5 family. M99686 germ line was most frequently used and the next most frequently used, were X92224/J, L21967 and L21964. A similar order was seen in patients. Among the clones, 20 sets of clones showed the same base sequence and this was frequent between V(H)2 and V(H)5. There was one set, which showed almost the same base sequence between different patients, and the homology was 99.5%. Twenty sets of clones that had the same base sequence showed high similarity to the germ line (94 - 100%). Among these, the clones that utilized the M99686 germ line were 4 sets which were most frequent. The 3-dimensional structure of one of these clones showed typical beta, sheet structure of immunoglobulin chains.
Conclusion: The IgM transcripts expressed by the B cells in the peripheral blood of KD patients in the acute phase of the disease clearly showed an oligoclonal expansion, suggesting that KD is caused not by stimulation of a superantigen, but rather by a conventional antigen.
Keywords: B cell; Kawasaki disease; conventional antigen; oligoclonal expansion; superantigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children: Clinical observations of 50 cases. Jpn J Allergol. 1967;16:178–222. - PubMed
-
- Freeman AF, Shulman ST. Recent developments in Kawasaki disease. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2001;14:357–361. - PubMed
-
- Leung DY, Meissner HC, Fulton DR, Murray DL, Kotzin BL, Schlievert PM. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-secreting Staphylococcus aureus in Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet. 1993;342:1385–1388. - PubMed
-
- Rowley AH, Eckerley CA, Jäck HM, Shulman ST, Baker SC. IgA plasma cells in vascular tissue of patients with Kawasaki syndrome. J Immunol. 1997;159:5946–5955. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

