Current status of thalidomide and CC-5013 in the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer
- PMID: 19719457
- PMCID: PMC6415974
- DOI: 10.2174/187152009789735017
Current status of thalidomide and CC-5013 in the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer
Abstract
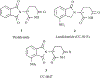
Thalidomide is emerging as a potentially important therapeutic option in the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Although the mechanism of action of this agent remains elusive in malignancies of the prostate, recent data has indicated that thalidomide may play a role in inflammation, immunomodulation, and anti-angiogenesis. Lenalidomide (CC-5013), a thalidomide analogue with improved activity and safety profile in certain disease contexts, is in the early stages of development in prostate cancer. This review will provide the current status of the history, mechanism, metabolism, and clinical use of thalidomide in metastatic prostate cancer. It will also describe the mechanism and clinical use of lenalidomide as it pertains to malignancies of the prostate.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A; Siegel R; Ward E; Hao Y; Xu J; Murray T; Thun MJ Cancer statistics:2008. CA Cancer J. Clin., 2008, 58(2), 71–96. - PubMed
-
- Petrylak DP; Tangen CM; Hussain MH; Lara PN Jr.; Jones JA; Taplin ME; Burch PA; Berry D; Moinpour C; Kohli M; Benson MC; Small EJ; Raghavan D; Crawford ED Docetaxel and estramustine compared with mitoxantrone and prednisone for advanced refractory prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med, 2004,351(15), 1513–20. - PubMed
-
- Tannock IF; de Wit R; Berry WR; Horti J; Pluzanska A; Chi KN; Oudard S; Theodore C; James ND; Turesson I; Rosenthal MA; Eisenberger MA Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351(15), 1502–12. - PubMed
-
- Lenz W; Pfeiffer R; Kosenow W; Hayman D Thalidomide and [26] congenital abnormalities. Lancet, 1962, 27945–46.
-
- McBride W Thalidomide and congenital abnormalities. Lancet, 1961,
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

