Novel antagonists for proteinase-activated receptor 2: inhibition of cellular and vascular responses in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 19719785
- PMCID: PMC2795266
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00342.x
Novel antagonists for proteinase-activated receptor 2: inhibition of cellular and vascular responses in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background and purpose: Proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR(2)) is a G-protein coupled receptor associated with many pathophysiological functions. To date, the development of PAR(2) antagonists has been limited. Here, we identify a number of novel peptide-mimetic PAR(2) antagonists and demonstrate inhibitory effects on PAR(2)-mediated intracellular signalling pathways and vascular responses.
Experimental approach: The peptide-mimetic compound library based on the structures of PAR(2) agonist peptides were screened for inhibition of PAR(2)-induced calcium mobilisation in human keratinocytes. Representative compounds were further evaluated by radioligand binding and inhibition of NFkappaB transcriptional activity and IL-8 production. The vascular effects of the antagonists were assessed using in vitro and in vivo models.
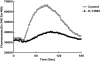
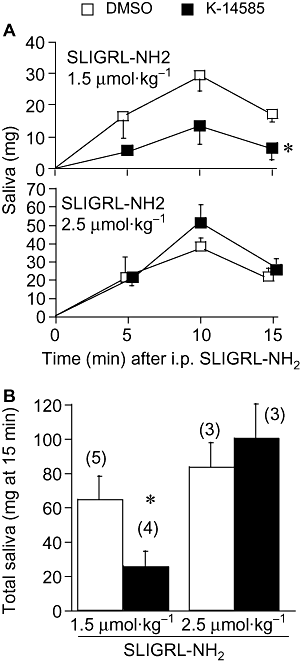
Key results: Two compounds, K-12940 and K-14585, significantly reduced SLIGKV-induced Ca(2+) mobilisation in primary human keratinocytes. Both K-12940 and K-14585 exhibited competitive inhibition for the binding of a high-affinity radiolabelled PAR(2)-ligand, [(3)H]-2-furoyl-LIGRL-NH(2), to human PAR(2) with K(i) values of 1.94 and 0.627 microM respectively. NFkappaB reporter activity and IL-8 production were also significantly reduced. Furthermore, relaxation of rat-isolated aorta induced by SLIGRL-NH(2) was inhibited competitively by K-14585. K-14585 also significantly lowered plasma extravasation in the dorsal skin of guinea pigs and reduced salivation in mice.
Conclusions and implications: K-12940 and K-14585 antagonized PAR(2) competitively, resulting in inhibition of PAR(2)-mediated signalling and physiological responses both in vitro and in vivo. These peptide-mimetic PAR(2) antagonists could be useful in evaluating PAR(2)-mediated biological events and might lead to a new generation of therapeutically useful antagonists.
Figures

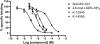
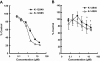



Similar articles
-
Dual effect of the novel peptide antagonist K-14585 on proteinase-activated receptor-2-mediated signalling.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;158(7):1695-704. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00415.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19917067 Free PMC article.
-
Potent and metabolically stable agonists for protease-activated receptor-2: evaluation of activity in multiple assay systems in vitro and in vivo.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Jun;309(3):1098-107. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.061010. Epub 2004 Feb 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. PMID: 14976227
-
Proteinase-activated receptor-2 activating peptides: distinct canine coronary artery receptor systems.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Dec;293(6):H3279-89. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00519.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17766477
-
Protease-activated receptor-2 antagonists and agonists.Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003 Mar;1(1):73-82. doi: 10.2174/1568016033356698. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003. PMID: 15317292 Review.
-
Discovery of potent peptide-mimetic antagonists for the human thrombin receptor, protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1).Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003 Mar;1(1):13-36. doi: 10.2174/1568016033356724. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003. PMID: 15317288 Review.
Cited by
-
Protease and protease-activated receptor-2 signaling in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis.Yonsei Med J. 2010 Nov;51(6):808-22. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.6.808. Yonsei Med J. 2010. PMID: 20879045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating human proteinase activated receptor 2 with a novel antagonist (GB88) and agonist (GB110).Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;165(5):1413-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01610.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21806599 Free PMC article.
-
Development of highly potent protease-activated receptor 2 agonists via synthetic lipid tethering.FASEB J. 2013 Apr;27(4):1498-510. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-217323. Epub 2013 Jan 4. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23292071 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesia for Sheep in Commercial Production: Where to Next?Animals (Basel). 2021 Apr 14;11(4):1127. doi: 10.3390/ani11041127. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interdicting protease-activated receptor-2-driven inflammation with cell-penetrating pepducins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 17;108(20):8491-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017091108. Epub 2011 May 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21536878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AlAni B, Saifeddine M, Hollenberg MD. Detection of functional receptors for the proteinase-activated-receptor-2-activating polypeptide, SLIGRL-NH2, in rat vascular and gastric smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995;73:1203–1207. - PubMed
-
- Blackhart BD, Ruslim-Litrus L, Lu CC, Alves VL, Teng W, Scarborough RM, et al. Extracellular mutations of protease-activated receptor-1 result in differential activation by thrombin and thrombin receptor agonist peptide. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;58:1178–1187. - PubMed
-
- Bushell TJ, Plevin R, Cobb S, Irving AJ. Characterization of proteinase-activated receptor 2 signalling and expression in rat hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. Neuropharmacology. 2006;50:714–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

