Evolution of opsins and phototransduction
- PMID: 19720651
- PMCID: PMC2781858
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0051
Evolution of opsins and phototransduction
Abstract
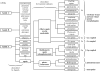
Opsins are the universal photoreceptor molecules of all visual systems in the animal kingdom. They can change their conformation from a resting state to a signalling state upon light absorption, which activates the G protein, thereby resulting in a signalling cascade that produces physiological responses. This process of capturing a photon and transforming it into a physiological response is known as phototransduction. Recent cloning techniques have revealed the rich and diverse nature of these molecules, found in organisms ranging from jellyfish to humans, functioning in visual and non-visual phototransduction systems and photoisomerases. Here we describe the diversity of these proteins and their role in phototransduction. Then we explore the molecular properties of opsins, by analysing site-directed mutants, strategically designed by phylogenetic comparison. This site-directed mutant approach led us to identify many key features in the evolution of the photoreceptor molecules. In particular, we will discuss the evolution of the counterion, the reduction of agonist binding to the receptor, and the molecular properties that characterize rod opsins apart from cone opsins. We will show how the advances in molecular biology and biophysics have given us insights into how evolution works at the molecular level.
Figures

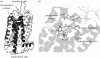
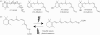
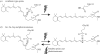

References
-
- Arendt D.2003Evolution of eyes and photoreceptor cell types. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 47, 563–571 - PubMed
-
- Arendt D., Tessmar-Raible K., Snyman H., Dorresteijn A. W., Wittbrodt J.2004Ciliary photoreceptors with a vertebrate-type opsin in an invertebrate brain. Science 306, 869–871 (doi:10.1126/science.1099955) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barnard A. R., Hattar S., Hankins M. W., Lucas R. J.2006Melanopsin regulates visual processing in the mouse retina. Curr. Biol. 16, 389–395 (doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.12.045) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beck M., Sakmar T. P., Siebert F.1998Spectroscopic evidence for interaction between transmembrane helices 3 and 5 in rhodopsin. Biochemistry 37, 7630–7639 (doi:10.1021/bi9801560) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
