Yersinia pseudotuberculosis virulence determinants invasin, YopE, and YopT modulate RhoG activity and localization
- PMID: 19720752
- PMCID: PMC2772528
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00850-09
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis virulence determinants invasin, YopE, and YopT modulate RhoG activity and localization
Abstract
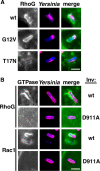
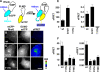
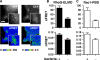
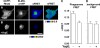
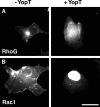
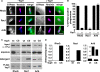
The Yersinia pseudotuberculosis surface protein invasin binds to multiple beta1 integrins with high affinity, leading to misregulation of Rac1 activity. Upon host cell binding, alteration of Rho GTPase activity results from the action of several Yersinia outer proteins (Yops) that are translocated into the cytoplasm. We report here that three virulence determinants encoded by Y. pseudotuberculosis manipulate the Rho GTPase RhoG. Y. pseudotuberculosis binding to cells caused robust recruitment of RhoG to the site of attachment, which required high-affinity invasin-beta1 integrin association. Furthermore, inactivation of RhoG significantly reduced the efficiency of invasin-mediated bacterial internalization. To investigate the activation state of RhoG, a fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based activation biosensor was developed and used to show distinct spatial activation of RhoG at the site of bacterial attachment. The biosensor was also used to show efficient RhoG inactivation by Y. pseudotuberculosis YopE, a potent Rho GTPase activating protein. Additionally, RhoG mislocalization by the prenylcysteine endoprotease YopT was demonstrated by two independent assays. Functional bacterial uptake experiments demonstrated that RhoG activation can bypass a deficit in Rac1 activity. Interestingly, increasing the size of the particle gave results more consistent with a linear pathway, in which RhoG acts as an upstream activator of Rac1, indicating that increased surface area introduces constraints on the signaling pathways required for efficient internalization. Taken together, these data demonstrate the misregulation of RhoG by multiple Y. pseudotuberculosis virulence determinants. Since RhoG is imperative for proper neutrophil function, this misregulation may represent a unique mechanism by which Yersinia species dampen the immune response.
Figures
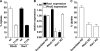
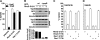

References
-
- Alrutz, M. A., A. Srivastava, K. W. Wong, C. D'Souza-Schorey, M. Tang, L. E. Ch'Ng, S. B. Snapper, and R. R. Isberg. 2001. Efficient uptake of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis via integrin receptors involves a Rac1-Arp 2/3 pathway that bypasses N-WASP function. Mol. Microbiol. 42:689-703. - PubMed
-
- Black, D. S., and J. B. Bliska. 2000. The RhoGAP activity of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis cytotoxin YopE is required for antiphagocytic function and virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 37:515-527. - PubMed
-
- Brunet, N., A. Morin, and B. Olofsson. 2002. RhoGDI-3 regulates RhoG and targets this protein to the Golgi complex through its unique N-terminal domain. Traffic 3:342-357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

