Patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis display impaired Th1 responses and enhanced regulatory T-cell levels in response to an outbreak of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis M and Ra strains
- PMID: 19720756
- PMCID: PMC2772532
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00224-09
Patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis display impaired Th1 responses and enhanced regulatory T-cell levels in response to an outbreak of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis M and Ra strains
Abstract
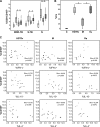
In Argentina, multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) outbreaks emerged among hospitalized patients with AIDS in the early 1990s and thereafter disseminated to the immunocompetent community. Epidemiological, bacteriological, and genotyping data allowed the identification of certain MDR Mycobacterium tuberculosis outbreak strains, such as the so-called strain M of the Haarlem lineage and strain Ra of the Latin America and Mediterranean lineage. In the current study, we evaluated the immune responses induced by strains M and Ra in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with active MDR-TB or fully drug-susceptible tuberculosis (S-TB) and in purified protein derivative-positive healthy controls (group N). Our results demonstrated that strain M was a weaker gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) inducer than H37Rv for group N. Strain M induced the highest interleukin-4 expression in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from MDR- and S-TB patients, along with the lowest cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activity in patients and controls. Hence, impairment of CTL activity is a hallmark of strain M and could be an evasion mechanism employed by this strain to avoid the killing of macrophages by M-specific CTL effectors. In addition, MDR-TB patients had an increased proportion of circulating regulatory T cells (Treg cells), and these cells were further expanded upon in vitro M. tuberculosis stimulation. Experimental Treg cell depletion increased IFN-gamma expression and CTL activity in TB patients, with M- and Ra-induced CTL responses remaining low in MDR-TB patients. Altogether, these results suggest that immunity to MDR strains might depend upon a balance between the individual host response and the ability of different M. tuberculosis genotypes to drive Th1 or Th2 profiles.
Figures
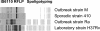

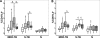
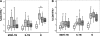


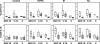
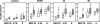
References
-
- Aita, J., L. Barrera, A. Reniero, B. López, J. Biglione, G. Weisburd, J. C. Rajmil, C. Largacha, and V. Ritacco. 1996. Hospital transmission of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Rosario, Argentina. Medicina (Buenos Aires) 56:48-50. - PubMed
-
- Betts, M. R., J. M. Brenchley, D. A. Price, S. C. De Rosa, D. C. Douek, M. Roederer, and R. A. Koup. 2003. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. J. Immunol. Methods 281:65-78. - PubMed
-
- Boyum, A. 1968. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of mononuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 97(Suppl.):77-89. - PubMed
-
- Castro, A. Z., B. M. Díaz-Bardalez, E. C. Oliveira, R. C. García, J. B. Afiune, I. A. Paschoal, and L. M. Santos. 2005. Abnormal production of transforming growth factor beta and interferon gamma by peripheral blood cells of patients with multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis in Brazil. J. Infect. 51:318-324. - PubMed
-
- Caws, M., G. Thwaites, S. Dunstan, T. R. Hawn, N. T. Lan, N. T. Thuong, K. Stepniewska, M. N. Huyen, N. D. Bang, T. H. Loc, S. Gagneux, D. van Soolingen, K. Kremer, M. van der Sande, P. Small, P. T. Anh, N. T. Chinh, H. T. Quy, N. T. Duyen, D. Q. Tho, N. T. Hieu, E. Torok, T. T. Hien, N. H. Dung, N. T. Nhu, P. M. Duy, N. van Vinh Chau, and J. Farrar. 2008. The influence of host and bacterial genotype on the development of disseminated disease with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 4:e1000034. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

