Fibroblast growth factor-21 is induced in human skeletal muscles by hyperinsulinemia
- PMID: 19720803
- PMCID: PMC2780875
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0713
Fibroblast growth factor-21 is induced in human skeletal muscles by hyperinsulinemia
Abstract
Objective: Fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF-21) is a potent metabolic regulator, which in animal models has been shown to improve glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Recently, FGF-21 was shown to be expressed and secreted from murine muscle cells in response to insulin stimulation.
Research design and methods: We studied muscular FGF-21 expression and plasma FGF-21 after acute insulin stimulation in young healthy men during a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. Furthermore, we investigated systemic levels and muscle FGF-21 expression in humans with or without insulin resistance and chronic elevated insulin.
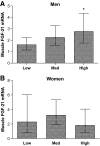
Results: FGF-21 was barely detectable in young healthy men before insulin infusion. After 3 or 4 h of insulin infusion during a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp, muscular FGF-21 expression increased significantly. Plasma FGF-21 followed the same pattern. In individuals with chronic elevated insulin, muscular FGF-21 expression was associated with hyperinsulinemia in men but not in women. In plasma, hyperinsulinemia and fasting glucose were positively associated with plasma FGF-21 while plasma FGF-21 correlated negatively with HDL cholesterol. No associations between muscle and plasma FGF-21 were found in the individuals with chronic hyperinsulinemia.
Conclusions: FGF-21 is expressed in human skeletal muscle in response to insulin stimulation, suggesting that FGF-21 is an insulin-regulated myokine. In support, we found an association between chronic hyperinsulinemia and levels of FGF-21.
Figures

References
-
- Moore DD: Physiology: sister act. Science 2007; 316: 1436– 1438 - PubMed
-
- Kharitonenkov A, Shanafelt AB: Fibroblast growth factor-21 as a therapeutic agent for metabolic diseases. Biodrugs 2008; 22: 37– 44 - PubMed
-
- Kharitonenkov A, Shiyanova TL, Koester A, Ford AM, Micanovic R, Galbreath EJ, Sandusky GE, Hammond LJ, Moyers JS, Owens RA, Gromada J, Brozinick JT, Hawkins ED, Wroblewski VJ, Li DS, Mehrbod F, Jaskunas SR, Shanafelt AB: FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1627– 1635 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kharitonenkov A, Wroblewski VJ, Koester A, Chen YF, Clutinger CK, Tigno XT, Hansen BC, Shanafelt AB, Etgen GJ: The metabolic state of diabetic monkeys is regulated by fibroblast growth factor-21. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 774– 781 - PubMed
-
- Coskun T, Bina HA, Schneider MA, Dunbar JD, Hu CC, Chen Y, Moller DE, Kharitonenkov A: Fibroblast growth factor 21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology 2008; 149: 6018– 6027 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

