MAP kinase signaling antagonizes PAR-1 function during polarization of the early Caenorhabditis elegans embryo
- PMID: 19720857
- PMCID: PMC2778991
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.106716
MAP kinase signaling antagonizes PAR-1 function during polarization of the early Caenorhabditis elegans embryo
Abstract
PAR proteins (partitioning defective) are major regulators of cell polarity and asymmetric cell division. One of the par genes, par-1, encodes a Ser/Thr kinase that is conserved from yeast to mammals. In Caenorhabditis elegans, par-1 governs asymmetric cell division by ensuring the polar distribution of cell fate determinants. However the precise mechanisms by which PAR-1 regulates asymmetric cell division in C. elegans remain to be elucidated. We performed a genomewide RNAi screen and identified six genes that specifically suppress the embryonic lethal phenotype associated with mutations in par-1. One of these suppressors is mpk-1, the C. elegans homolog of the conserved mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase ERK. Loss of function of mpk-1 restored embryonic viability, asynchronous cell divisions, the asymmetric distribution of cell fate specification markers, and the distribution of PAR-1 protein in par-1 mutant embryos, indicating that this genetic interaction is functionally relevant for embryonic development. Furthermore, disrupting the function of other components of the MAPK signaling pathway resulted in suppression of par-1 embryonic lethality. Our data therefore indicates that MAP kinase signaling antagonizes PAR-1 signaling during early C. elegans embryonic polarization.
Figures
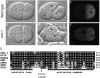
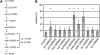
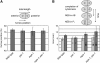

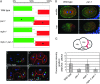
References
-
- Basham, S. E., and L. S. Rose, 1999. Mutations in ooc-5 and ooc-3 disrupt oocyte formation and the reestablishment of asymmetric PAR protein localization in two-cell Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Dev. Biol. 215 253–263. - PubMed
-
- Benton, R., and D. St Johnston, 2003. Drosophila PAR-1 and 14–3-3 inhibit Bazooka/PAR-3 to establish complementary cortical domains in polarized cells. Cell 115 691–704. - PubMed
-
- Boyd, L., S. Guo, D. Levitan, D. T. Stinchcomb and K. J. Kemphues, 1996. PAR-2 is asymmetrically distributed and promotes association of P granules and PAR-1 with the cortex in C. elegans embryos. Development 122 3075–3084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

