Redox signaling between DNA repair proteins for efficient lesion detection
- PMID: 19720997
- PMCID: PMC2741234
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908059106
Redox signaling between DNA repair proteins for efficient lesion detection
Abstract
Base excision repair (BER) enzymes maintain the integrity of the genome, and in humans, BER mutations are associated with cancer. Given the remarkable sensitivity of DNA-mediated charge transport (CT) to mismatched and damaged base pairs, we have proposed that DNA repair glycosylases (EndoIII and MutY) containing a redox-active [4Fe4S] cluster could use DNA CT in signaling one another to search cooperatively for damage in the genome. Here, we examine this model, where we estimate that electron transfers over a few hundred base pairs are sufficient for rapid interrogation of the full genome. Using atomic force microscopy, we found a redistribution of repair proteins onto DNA strands containing a single base mismatch, consistent with our model for CT scanning. We also demonstrated in Escherichia coli a cooperativity between EndoIII and MutY that is predicted by the CT scanning model. This relationship does not require the enzymatic activity of the glycosylase. Y82A EndoIII, a mutation that renders the protein deficient in DNA-mediated CT, however, inhibits cooperativity between MutY and EndoIII. These results illustrate how repair proteins might efficiently locate DNA lesions and point to a biological role for DNA-mediated CT within the cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
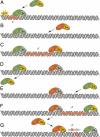
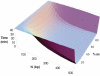
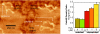
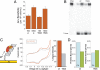
Comment in
-
Finding needles in DNA stacks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 22;106(38):16010-1. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909136106. Epub 2009 Sep 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19805252 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Demple B, Harrison L. Repair of oxidative damage to DNA: Enzymology and biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:915–948. - PubMed
-
- Francis AW, Helquist SA, Kool ET, David SS. Probing the requirements for recognition and catalysis in Fpg and MutY with nonpolar adenine isosteres. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:16235–16242. - PubMed
-
- Fromme JC, Banerjee A, Huang SJ, Verdine GL. Structural basis for removal of adenine mispaired with 8-oxoguanine by MutY adenine glycosylase. Nature. 2004;427:652–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

