Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options
- PMID: 19721819
- PMCID: PMC2724665
- DOI: 10.2174/157015909787602823
Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options
Abstract
Free radicals are common outcome of normal aerobic cellular metabolism. In-built antioxidant system of body plays its decisive role in prevention of any loss due to free radicals. However, imbalanced defense mechanism of antioxidants, overproduction or incorporation of free radicals from environment to living system leads to serious penalty leading to neuro-degeneration. Neural cells suffer functional or sensory loss in neurodegenerative diseases. Apart from several other environmental or genetic factors, oxidative stress (OS) leading to free radical attack on neural cells contributes calamitous role to neuro-degeneration. Though, oxygen is imperative for life, imbalanced metabolism and excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation end into a range of disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, aging and many other neural disorders. Toxicity of free radicals contributes to proteins and DNA injury, inflammation, tissue damage and subsequent cellular apoptosis. Antioxidants are now being looked upon as persuasive therapeutic against solemn neuronal loss, as they have capability to combat by neutralizing free radicals. Diet is major source of antioxidants, as well as medicinal herbs are catching attention to be commercial source of antioxidants at present. Recognition of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapy to oxidative stress has been proved an effective tool in alteration of any neuronal damage as well as free radical scavenging. Antioxidants have a wide scope to sequester metal ions involved in neuronal plaque formation to prevent oxidative stress. In addition, antioxidant therapy is vital in scavenging free radicals and ROS preventing neuronal degeneration in post-oxidative stress scenario.
Keywords: ROS; amyloid; antioxidants; catalase; neurodegenerative diseases; oxidative stress; phagocytes.; rns.
Figures
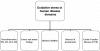


References
-
- Angelo D, Erene M, Rakez K, Saskia C, Milton IP, Charles G Glabe. Calcium dysregulation and membrane disruption as a ubiquitous neurotoxic mechanism of soluble amyloid Oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280(17):172–94. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf V, Franco G, Syed I, Zbigniew B, Syed A. Possible mechanism for the neuroprotective effects of l-Carnitine on methamphetamine-evoked neurotoxicity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006;993:197–207. - PubMed
-
- Barry H. Antioxidants in human health and disease. Annu. Rev. Nut. 1996;16:33–50. - PubMed
-
- Baynes JW. Role of oxidative stress in development of complications in diabetes. Diabetes. 1991;40:405–412. - PubMed
-
- Baynes JW, Thorpe SR. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: A new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes. 1999;48:1–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
