Regulation of Rnd3 localization and function by protein kinase C alpha-mediated phosphorylation
- PMID: 19723022
- PMCID: PMC2868966
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20082377
Regulation of Rnd3 localization and function by protein kinase C alpha-mediated phosphorylation
Abstract
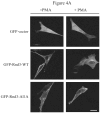
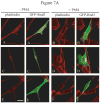
The Rnd proteins (Rnd1, Rnd2 and Rnd3/RhoE) form a distinct branch of the Rho family of small GTPases. Altered Rnd3 expression causes changes in cytoskeletal organization and cell cycle progression. Rnd3 functions to decrease RhoA activity, but how Rnd3 itself is regulated to cause these changes is still under investigation. Unlike other Rho family proteins, Rnd3 is regulated not by GTP/GDP cycling, but at the level of expression and by post-translational modifications such as prenylation and phosphorylation. We show in the present study that, upon PKC (protein kinase C) agonist stimulation, Rnd3 undergoes an electrophoretic mobility shift and its subcellular localization becomes enriched at internal membranes. These changes are blocked by inhibition of conventional PKC isoforms and do not occur in PKCalpha-null cells or to a non-phosphorylatable mutant of Rnd3. We further show that PKCalpha directly phosphorylates Rnd3 in an in vitro kinase assay. Additionally, we provide evidence that the phosphorylation status of Rnd3 has a direct effect on its ability to block signalling from the Rho-ROCK (Rho-kinase) pathway. These results identify an additional mechanism of regulation and provide clarification of how Rnd3 modulates Rho signalling to alter cytoskeletal organization.
Figures















References
-
- Hall A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998;279:509–514. - PubMed
-
- Nobes CD, Hall A. Rho, rac and cdc42 GTPases: regulators of actin structures, cell adhesion and motility. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995;23:456–459. - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ, Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992;70:389–399. - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ, Paterson HF, Johnston CL, Diekmann D, Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992;70:401–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM055279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- BB/E004083/2/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA109550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- BB/E004083/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- CA063071/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA071341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092240/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA92240/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA067771/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116034/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA109550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA067771/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA67771/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063071/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

