Inhibitory effects of armepavine against hepatic fibrosis in rats
- PMID: 19723340
- PMCID: PMC2741443
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-16-78
Inhibitory effects of armepavine against hepatic fibrosis in rats
Abstract
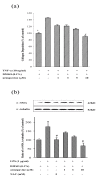
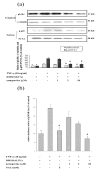
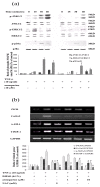
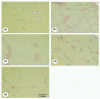
Activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) plays a crucial role in liver fibrogenesis. armepavine (Arm, C19H23O3N), an active compound from Nelumbo nucifera, has been shown to exert immunosuppressive effects on T lymphocytes and on lupus nephritic mice. The aim of this study was to investigate whether Arm could exert anti-hepatic fibrogenic effects in vitro and in vivo. A cell line of rat HSCs (HSC-T6) was stimulated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to evaluate the inhibitory effects of Arm. An in vivo therapeutic study was conducted in bile duct-ligated (BDL) rats. BDL rats were given Arm (3 or 10 mg/kg) by gavage twice daily for 3 weeks starting from the onset of BDL. Liver sections were taken for fibrosis scoring, immuno-fluorescence staining and quantitative real-time mRNA measurements. In vitro, Arm (1-10 microM) concentration-dependently attenuated TNF-alpha- and LPS-stimulated alpha-SMA protein expression and AP-1 activation by HSC-T6 cells without adverse cytotoxicity. Arm also suppressed TNF-alpha-induced collagen collagen deposition, NFkappaB activation and MAPK (p38, ERK1/2, and JNK) phosphorylations. In vivo, Arm treatment significantly reduced plasma AST and ALT levels, hepatic alpha-SMA expression and collagen contents, and fibrosis scores of BDL rats as compared with vehicle treatment. Moreover, Arm attenuated the mRNA expression levels of col 1alpha2, TGF-beta1, TIMP-1, ICAM-1, iNOS, and IL-6 genes, but up-regulated metallothionein genes. Our study results showed that Arm exerted both in vitro and in vivo antifibrotic effects in rats, possibly through anti-NF-kappaB activation pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of armepavine against hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide in rats.Phytother Res. 2012 Mar;26(3):344-53. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3539. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Phytother Res. 2012. PMID: 21717514
-
Antifibrotic effects of tetrandrine on hepatic stellate cells and rats with liver fibrosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Jan;22(1):99-111. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04361.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17201889
-
Antifibrotic effects of triptolide on hepatic stellate cells and dimethylnitrosamine-intoxicated rats.Phytother Res. 2011 Jul;25(7):990-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3381. Phytother Res. 2011. PMID: 21213358
-
Anti-fibrotic effects of thalidomide on hepatic stellate cells and dimethylnitrosamine-intoxicated rats.J Biomed Sci. 2006 May;13(3):403-18. doi: 10.1007/s11373-006-9079-5. Epub 2006 Apr 8. J Biomed Sci. 2006. PMID: 16604421
-
Liuweiwuling tablets attenuate BDL-induced hepatic fibrosis via modulation of TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:232-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.029. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28864168
Cited by
-
Complete biosynthesis of the bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids guattegaumerine and berbamunine in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Dec 21;118(51):e2112520118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2112520118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34903659 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel anti-inflammatory agents from Ayurvedic medicine for prevention of chronic diseases: "reverse pharmacology" and "bedside to bench" approach.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Oct;12(11):1595-653. doi: 10.2174/138945011798109464. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21561421 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal remedies for liver fibrosis: A review on the mode of action of fifty herbs.J Tradit Complement Med. 2017 Nov 22;8(3):352-360. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.07.002. eCollection 2018 Jul. J Tradit Complement Med. 2017. PMID: 29992106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnomedicine, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities of Uvaria chamae P. Beauv.: A comprehensive review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Aug;397(8):5421-5436. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03018-6. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38421410 Review.
-
Suppression of nitric oxide production from nasal fibroblasts by metabolized clarithromycin in vitro.J Inflamm (Lond). 2010 Nov 23;7:56. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-7-56. J Inflamm (Lond). 2010. PMID: 21092318 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

