Pigment epithelium-derived factor maintains retinal pigment epithelium function by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor-R2 signaling through gamma-secretase
- PMID: 19723623
- PMCID: PMC2781573
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.032391
Pigment epithelium-derived factor maintains retinal pigment epithelium function by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor-R2 signaling through gamma-secretase
Abstract
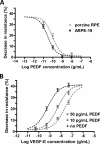
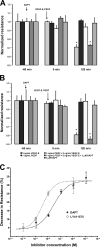
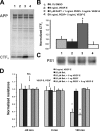
Wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) attacks the integrity of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) barrier system. The pathogenic process was hypothesized to be mediated by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and antagonized by pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF). To dissect these functional interactions, monolayer cultures of RPE cells were established, and changes in transepithelial resistance were evaluated after administration of PEDF, placenta growth factor (VEGF-R1 agonist), and VEGF-E (VEGF-R2 agonist). A recently described mechanism of VEGF inhibition in endothelia required the release of VEGF-R1 intracellular domain by gamma-secretase. To evaluate this pathway in the RPE, cells were pretreated with inhibitors DAPT or LY411575. Processing of VEGF receptors was assessed by Western blot analysis. Administration of VEGF-E rapidly increased RPE permeability, and PEDF inhibited the VEGF-E response dose-dependently. Both gamma-secretase antagonists prevented the inhibitory effects of PEDF. The co-administration of PEDF and VEGF-E depleted the amount of VEGF-R2 in the membrane and increased the amount of VEGF-R2 ectodomain in the media. Therefore, the inhibitory effect of PEDF appears to be mediated via the processing of VEGF-R2 by gamma-secretase. gamma-Secretase generates the amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide of Alzheimer disease from its precursor (amyloid precursor protein). This peptide is also a component of drusen in dry AMD. The results support the hypothesis that misregulation of gamma-secretase may not only lead to Abeta deposits in dry AMD but can also be damaging to RPE function by blocking the protective effects of PEDF to prevent VEGF from driving the dry to wet AMD transition.
Figures


References
-
- Tranos P. G., Wickremasinghe S. S., Stangos N. T., Topouzis F., Tsinopoulos I., Pavesio C. E. (2004) Surv. Ophthalmol. 49, 470–490 - PubMed
-
- Augustin A. J., Puls S., Offermann I. (2007) Retina 27, 133–140 - PubMed
-
- Marmor M. F. (1999) Documenta Ophthalmologica 97, 239–249 - PubMed
-
- Gragoudas E. S., Adamis A. P., Cunningham E. T., Jr., Feinsod M., Guyer D. R. (2004) N. Engl. J. Med. 351, 2805–2816 - PubMed
-
- Heier J. S., Antoszyk A. N., Pavan P. R., Leff S. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Ciulla T. A., Dreyer R. F., Gentile R. C., Sy J. P., Hantsbarger G., Shams N. (2006) Ophthalmology 113, 642, e641–644 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

