MicroRNA-206 targets notch3, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell migration and focus formation
- PMID: 19723635
- PMCID: PMC2797263
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.046862
MicroRNA-206 targets notch3, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell migration and focus formation
Abstract
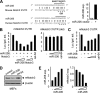
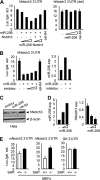
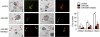
MicroRNAs contribute to cancer development by acting as oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. However, only a few microRNA target genes were determined. We identified a nearly perfect complementarity between miR-206 and the 3'-untranslated regions of both mouse and human notch3. Expression of miR-206 decreased the luciferase activity dose-dependently when cotransfected with the mouse or human notch3 3'-untranslated region-luciferase reporter containing the miR-206 target site in HeLa cells. This suppression was relieved by deletion and mutation of the miR-206-binding site and was partially recovered by expression of notch3 or by a specific inhibitor of miR-206. Interestingly, overexpression of miR-206 decreased the levels of both Notch3 protein and mRNA. Expression of miR-206 markedly induced apoptotic cell death and blocked the anti-apoptotic activity of Notch3. In addition, ectopic expression of miR-206 inhibited HeLa cell migration and focus formation. Therefore, we identified miR-206 as a pro-apoptotic activator of cell death, which was associated with its inhibition of notch3 signaling and tumor formation. The inhibition of cancer cell migration and focus formation by miR-206 strongly suggests that miR-206 may function as a novel tumor suppressor.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

