Presenilins, Notch dose control the fate of pancreatic endocrine progenitors during a narrow developmental window
- PMID: 19723764
- PMCID: PMC2751975
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1800209
Presenilins, Notch dose control the fate of pancreatic endocrine progenitors during a narrow developmental window
Abstract
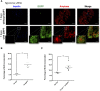
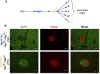
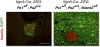
Canonical Notch signaling is thought to control the endocrine/exocrine decision in early pancreatic progenitors. Later, RBP-Jkappa interacts with Ptf1a and E12 to promote acinar differentiation. To examine the involvement of Notch signaling in selecting specific endocrine lineages, we deregulated this pathway by targeted deletion of presenilin1 and presenilin2, the catalytic core of gamma-secretase, in Ngn3- or Pax6-expressing endocrine progenitors. Surprisingly, whereas Pax6(+) progenitors were irreversibly committed to the endocrine fate, we discovered that Ngn3(+) progenitors were bipotential in vivo and in vitro. When presenilin amounts are limiting, Ngn3(+) progenitors default to an acinar fate; subsequently, they expand rapidly to form the bulk of the exocrine pancreas. gamma-Secretase inhibitors confirmed that enzymatic activity was required to block acinar fate selection by Ngn3 progenitors. Genetic interactions identified Notch2 as the substrate, and suggest that gamma-secretase and Notch2 act in a noncanonical titration mechanism to sequester RBP-Jkappa away from Ptf1a, thus securing selection of the endocrine fate by Ngn3 progenitors. These results revise the current view of pancreatic cell fate hierarchy, establish that Ngn3 is not in itself sufficient to commit cells to the endocrine fate in the presence of Ptf1a, reveal a noncanonical action for Notch2 protein in endocrine cell fate selection, and demonstrate that acquisition of an endocrine fate by Ngn3(+) progenitors is gamma-secretase-dependent until Pax6 expression begins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early pancreatic islet fate and maturation is controlled through RBP-Jκ.Sci Rep. 2016 May 31;6:26874. doi: 10.1038/srep26874. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27240887 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenin 3 Expressing Cells in the Human Exocrine Pancreas Have the Capacity for Endocrine Cell Fate.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 19;10(8):e0133862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133862. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26288179 Free PMC article.
-
Notch-mediated post-translational control of Ngn3 protein stability regulates pancreatic patterning and cell fate commitment.Dev Biol. 2013 Apr 1;376(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.01.021. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23370147
-
Direct lineage tracing reveals the ontogeny of pancreatic cell fates during mouse embryogenesis.Mech Dev. 2003 Jan;120(1):35-43. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(02)00330-1. Mech Dev. 2003. PMID: 12490294 Review.
-
Promoting ectopic pancreatic fates: pancreas development and future diabetes therapies.Clin Genet. 2008 Oct;74(4):316-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2008.01081.x. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Clin Genet. 2008. PMID: 18783407 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improved in vivo imaging method for individual islets across the mouse pancreas reveals a heterogeneous insulin secretion response to glucose.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):603. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79727-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33436691 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional control of mammalian pancreas organogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Jul;71(13):2383-402. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1510-2. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24221136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genes Associated with Pancreas Development and Function Maintain Open Chromatin in iPSCs Generated from Human Pancreatic Beta Cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2017 Nov 14;9(5):1395-1405. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.09.020. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Stem Cell Reports. 2017. PMID: 29107594 Free PMC article.
-
Nkx6.1 controls a gene regulatory network required for establishing and maintaining pancreatic Beta cell identity.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003274. Epub 2013 Jan 31. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23382704 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-edited human stem cell-derived beta cells: a powerful tool for drilling down on type 2 diabetes GWAS biology.F1000Res. 2016 Jul 15;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-1711. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.8682.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27508066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apelqvist Å, Li H, Sommer L, Beatus P, Anderson DJ, Honjo T, Hrabe de Angelis M, Lendahl U, Edlund H. Notch signalling controls pancreatic cell differentiation. Nature. 1999;400:877–881. - PubMed
-
- Cheng HT, Miner JH, Lin M, Tansey MG, Roth K, Kopan R. γ-Secretase activity is dispensable for mesenchyme-to-epithelium transition but required for podocyte and proximal tubule formation in developing mouse kidney. Development. 2003;130:5031–5042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
