Oxidative stress and the muscle reflex in heart failure
- PMID: 19723775
- PMCID: PMC2790260
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.177071
Oxidative stress and the muscle reflex in heart failure
Abstract
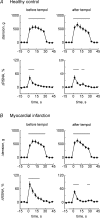
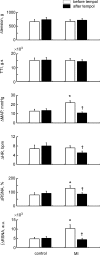
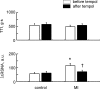
Muscle contraction stimulates thin fibre muscle afferents and evokes a reflex increase in blood pressure. In heart failure (HF) this reflex is accentuated. Of note, superoxide and other reactive oxygen species are increased in HF. In this report, we tested the hypothesis that excess superoxide contributes to the exaggerated muscle reflex in HF. HF was induced in rats by coronary artery ligation. Electrically induced 30 s hindlimb muscle contraction in decerebrate rats with myocardial infarction (MI) (left ventricular fractional shortening (FS) = 24 +/- 1%; n = 15) evoked larger (P < 0.05) increases in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) as compared to control rats (FS = 47 +/- 1%; n = 14). In the MI rats, the pressor and RSNA responses to contraction were reduced by intra-arterial injection into the hindlimb circulation of tempol (10 mg), a superoxide dismutase mimetic (DeltaMAP: 22 +/- 2 vs. 11 +/- 1 mmHg; integral DeltaRSNA: 1032 +/- 204 vs. 431 +/- 73 arbitrary units (a.u.); before vs. after tempol; P < 0.05). Tempol also attenuated the RSNA response to 1 min intermittent (1-4 s stimulation to relaxation) bouts of static contraction in the MI rats (116 +/- 17 vs. 72 +/- 11 a.u.; P < 0.05; n = 16). In the control rats, tempol had no effect on these responses. These results suggest that excess superoxide in HF sensitizes mechanically sensitive muscle afferents engaged during contraction. We hypothesize that oxidative stress contributes to the exaggerated muscle reflex in HF.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bradykinin receptor blockade reduces sympathetic nerve response to muscle contraction in rats with ischemic heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):H1438-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00558.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20207818 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mechanosensory role for acid sensing ion channel subtype 1a in evoking the exercise pressor reflex in rats with heart failure.J Physiol. 2022 May;600(9):2105-2125. doi: 10.1113/JP282923. Epub 2022 Apr 13. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35343594 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress exaggerates skeletal muscle contraction-evoked reflex sympathoexcitation in rats with hypertension induced by angiotensin II.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Jan 1;304(1):H142-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00423.2012. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23086992
-
Novel role for purinergic 2× subtype 4 (P2X4) receptors in the exercise pressor reflex and mechanoreflex: Effect of heart failure.Auton Neurosci. 2025 Aug;260:103277. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2025.103277. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Auton Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40233602
-
Thromboxane A2 receptors contribute to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in male rats with heart failure.Physiol Rep. 2021 Sep;9(18):e15052. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15052. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34558221 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A differing role of oxidative stress in the regulation of central and peripheral hemodynamics during exercise in heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Nov 15;303(10):H1237-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00568.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22961867 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Blockade of ATP-sensitive potassium channels prevents the attenuation of the exercise pressor reflex by tempol in rats with ligated femoral arteries.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Aug 1;303(3):H332-40. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00310.2012. Epub 2012 May 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22636679 Free PMC article.
-
Maintained sympathetic reactivity but blunted pressor response to static handgrip exercise in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Clin Auton Res. 2025 Jun;35(3):487-500. doi: 10.1007/s10286-025-01114-y. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Clin Auton Res. 2025. PMID: 40000578 Free PMC article.
-
Neurovascular Dysregulation During Exercise in Type 2 Diabetes.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 13;12:628840. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.628840. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33927637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bradykinin receptor blockade reduces sympathetic nerve response to muscle contraction in rats with ischemic heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):H1438-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00558.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20207818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstead WM. Brain injury impairs ATP-sensitive K+ channel function in piglet cerebral arteries. Stroke. 1997;28:2273–2279. - PubMed
-
- Bauersachs J, Bouloumie A, Fraccarollo D, Hu K, Busse R, Ertl G. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic myocardial infarction despite increased vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase expression: role of enhanced vascular superoxide production. Circulation. 1999;100:292–298. - PubMed
-
- Beuckelmann DJ, Näbauer M, Erdmann E. Alterations of K+ currents in isolated human ventricular myocytes from patients with terminal heart failure. Circ Res. 1993;73:379–385. - PubMed
-
- Calabresi P, Mercuri NB, Bernardi G. Synaptic and intrinsic control of membrane excitability of neostriatal neurons. II. An in vitro analysis. J Neurophysiol. 1990;63:663–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

