Recent advances in understanding leptin signaling and leptin resistance
- PMID: 19724019
- PMCID: PMC2793049
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00274.2009
Recent advances in understanding leptin signaling and leptin resistance
Abstract
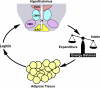
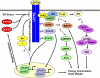
The brain controls energy homeostasis and body weight by integrating various metabolic signals. Leptin, an adipose-derived hormone, conveys critical information about peripheral energy storage and availability to the brain. Leptin decreases body weight by both suppressing appetite and promoting energy expenditure. Leptin directly targets hypothalamic neurons, including AgRP and POMC neurons. These leptin-responsive neurons widely connect to other neurons in the brain, forming a sophisticated neurocircuitry that controls energy intake and expenditure. The anorexigenic actions of leptin are mediated by LEPRb, the long form of the leptin receptor, in the hypothalamus. LEPRb activates both JAK2-dependent and -independent pathways, including the STAT3, PI 3-kinase, MAPK, AMPK, and mTOR pathways. These pathways act coordinately to form a network that fully mediates leptin response. LEPRb signaling is regulated by both positive (e.g., SH2B1) and negative (e.g., SOCS3 and PTP1B) regulators and by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Leptin resistance, a primary risk factor for obesity, likely results from impairment in leptin transport, LEPRb signaling, and/or the neurocircuitry of energy balance.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson KA, Ribar TJ, Lin F, Noeldner PK, Green MF, Muehlbauer MJ, Witters LA, Kemp BE, Means AR. Hypothalamic CaMKK2 contributes to the regulation of energy balance. Cell Metab 7: 377–388, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Andersson U, Filipsson K, Abbott CR, Woods A, Smith K, Bloom SR, Carling D, Small CJ. AMP-activated protein kinase plays a role in the control of food intake. J Biol Chem 279: 12005–12008, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Balthasar N, Coppari R, McMinn J, Liu SM, Lee CE, Tang V, Kenny CD, McGovern RA, Chua SC, Jr, Elmquist JK, Lowell BB. Leptin receptor signaling in POMC neurons is required for normal body weight homeostasis. Neuron 42: 983–991, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Banks AS, Davis SM, Bates SH, Myers MG., Jr Activation of downstream signals by the long form of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem 275: 14563–14572, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Huang W, Jaspan JB, Maness LM. Leptin enters the brain by a saturable system independent of insulin. Peptides 17: 305–311, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

