Photoacoustic tomography and sensing in biomedicine
- PMID: 19724102
- PMCID: PMC2872141
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/19/R01
Photoacoustic tomography and sensing in biomedicine
Abstract
Photoacoustics has been broadly studied in biomedicine, for both human and small animal tissues. Photoacoustics uniquely combines the absorption contrast of light or radio frequency waves with ultrasound resolution. Moreover, it is non-ionizing and non-invasive, and is the fastest growing new biomedical method, with clinical applications on the way. This review provides a brief recap of recent developments in photoacoustics in biomedicine, from basic principles to applications. The emphasized areas include the new imaging modalities, hybrid detection methods, photoacoustic contrast agents and the photoacoustic Doppler effect, as well as translational research topics.
Figures
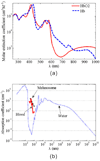



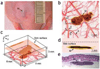




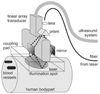


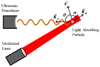

References
-
- Alexander Graham Bell On the production of sound by light. American Journal of Science. 1880;20:305.
-
- Kreuzer LB. Ultralow gas concentration infrared absorption spectroscopy. Journal of Applied Physics. 1971;42(7):2934–2943.
-
- Rosencwaig Allan. Photoacoustics and Photoacoustic Spectroscopy. New York: Wiley; 1980. Chemical analysis.
-
- Gusev VE, Karabutov AA, Hendzel Kevin. Laser Optoacoustics. AIP Press; 1993.
-
- Maugh Ii Thomas H. Photoacoustic spectroscopy: New uses for an old technique. Science. 1975;188(4183):38–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
