Complementary optical and nuclear imaging of caspase-3 activity using combined activatable and radio-labeled multimodality molecular probe
- PMID: 19725712
- PMCID: PMC2916017
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3207156
Complementary optical and nuclear imaging of caspase-3 activity using combined activatable and radio-labeled multimodality molecular probe
Abstract
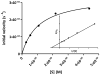
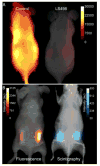
Based on the capability of modulating fluorescence intensity by specific molecular events, we report a new multimodal optical-nuclear molecular probe with complementary reporting strategies. The molecular probe (LS498) consists of tetraazacyclododecanetetraacetic acid (DOTA) for chelating a radionuclide, a near-infrared fluorescent dye, and an efficient quencher dye. The two dyes are separated by a cleavable peptide substrate for caspase-3, a diagnostic enzyme that is upregulated in dying cells. LS498 is radiolabeled with (64)Cu, a radionuclide used in positron emission tomography. In the native form, LS498 fluorescence is quenched until caspase-3 cleavage of the peptide substrate. Enzyme kinetics assay shows that LS498 is readily cleaved by caspase-3, with excellent enzyme kinetic parameters k(cat) and K(M) of 0.55+/-0.01 s(-1) and 1.12+/-0.06 microM, respectively. In mice, the initial fluorescence of LS498 is ten-fold less than control. Using radiolabeled (64)Cu-LS498 in a controlled and localized in-vivo model of caspase-3 activation, a time-dependent five-fold NIR fluorescence enhancement is observed, but radioactivity remains identical in caspase-3 positive and negative controls. These results demonstrate the feasibility of using radionuclide imaging for localizing and quantifying the distribution of molecular probes and optical imaging for reporting the functional status of diagnostic enzymes.
Figures
References
-
- Barbour RL, Graber HL, Chang J, Barbour SS, Koo PC, Aronson R. MRI-guided optical tomography:prospects and computation for a new imaging method. IEEE Comput Sci Eng. 1995;2:63–77.
-
- Barnett AH, Culver JP, Sorensen AG, Dale A, Boas DA. Robust inference of baseline optical properties of the human head with three-dimensional segmentation from magnetic resonance imaging. Appl Optics. 2003;42:3095–3108. - PubMed
-
- Pogue BW, Paulsen KD. High-resolution near-infrared tomographic imaging simulations of the rat cranium by use of apriori magnetic resonance imaging structural information. Opt Lett. 1998;23:1716–1718. - PubMed
-
- Culver J, Akers W, Achilefu S. Multimodality molecular imaging with combined optical and SPECT/PET modalities. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:169–172. - PubMed
-
- Edwards WB, Akers WJ, Ye Y, Cheney PP, Bloch S, Xu B, Laforest R, Achilefu S. Multimodal Imaging of Integrin Receptor-Positive Tumors by Bioluminescence, Fluorescence, Gamma Scintigraphy, and Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Using a Cyclic RGD Peptide Labeled with a Near-Infrared Fluorescent Dye and a Radionuclide. Mol Imaging. 2009;8:101–110. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

