Induction of therapeutic antibodies by vaccination against external loops of tumor-associated viral latent membrane protein
- PMID: 19726497
- PMCID: PMC2772700
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00578-09
Induction of therapeutic antibodies by vaccination against external loops of tumor-associated viral latent membrane protein
Abstract
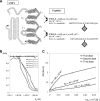
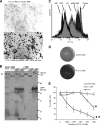
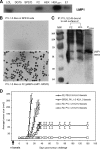
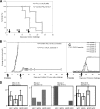
Some human herpesviruses (HHV) are etiological contributors to a wide range of malignant diseases. These HHV express latent membrane proteins (LMPs), which are type III membrane proteins consistently exposed at the cell surface in these malignancies. These LMPs have relatively large cytoplasmic domains but only short extracellular loops connecting transmembrane segments that are accessible at the surface of infected cells, but they do not elicit antibodies in the course of natural infection and tumorigenesis. We report here that conformational peptides mimicking two adjacent loops of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) LMP1 (2LS peptides) induce high-affinity antibodies with remarkable antitumor activities in mice. In active immunization experiments, LMP1-targeting 2LS vaccine conferred tumor protection in BALB/c mice. Moreover, this tumor protection is dependent upon a humoral anti-2LS immune response as demonstrated in DO11.10 (TCR-OVA) mice challenged with LMP1-expressing tumor and in SCID mice xenografted with human EBV-positive lymphoma cells. These data provide a proof of concept for 2LS immunization against short external loops of viral LMPs. This approach might possibly be extended to other infectious agents expressing type III membrane proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Restricted low-level human antibody responses against Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded latent membrane protein 1 in a subgroup of patients with EBV-associated diseases.J Infect Dis. 1999 May;179(5):1108-15. doi: 10.1086/314704. J Infect Dis. 1999. PMID: 10191211
-
Immune response of mice to a latency membrane protein 2 multiepitope antigen of Epstein-Barr virus applied as DNA vaccine and/or peptide vaccine.Acta Virol. 2013;57(1):51-8. doi: 10.4149/av_2013_01_51. Acta Virol. 2013. PMID: 23530824
-
Therapeutic LMP1 polyepitope vaccine for EBV-associated Hodgkin disease and nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Blood. 2003 Apr 15;101(8):3150-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3092. Epub 2002 Dec 5. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12468425
-
Role of LMP1 in immune control of EBV infection.Semin Cancer Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):455-60. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2001.0412. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001. PMID: 11669607 Review.
-
Multiple roles of LMP1 in Epstein-Barr virus induced immune escape.Semin Cancer Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):388-96. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.10.004. Epub 2008 Nov 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008. PMID: 19013244 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of EBV-Encoded LMP1 in the NPC Tumor Microenvironment: From Function to Therapy.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;11:640207. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.640207. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccination against Epstein-Barr Latent Membrane Protein 1 Protects against an Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated B Cell Model of Lymphoma.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jul 11;12(7):983. doi: 10.3390/biology12070983. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508413 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma therapeutics: oncoprotein targets and clinical implications.Med Oncol. 2025 Jan 31;42(3):59. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02610-x. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39888474 Review.
-
The C-Terminal Arm of the Human Papillomavirus Major Capsid Protein Is Immunogenic and Involved in Virus-Host Interaction.Structure. 2016 Jun 7;24(6):874-85. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.04.008. Structure. 2016. PMID: 27276427 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic implications of Epstein-Barr virus infection for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014 Sep 5;10:721-36. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S47434. eCollection 2014. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014. PMID: 25228810 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bernstein, D. I. 2001. Potential for immunotherapy in the treatment of herpesvirus infections. Herpes 8:8-11. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann, M. M., and T. F. Schulz. 2006. Regulation of intracellular signalling by the terminal membrane proteins of members of the Gammaherpesvirinae. J. Gen. Virol. 87:1047-1074. - PubMed
-
- Burton, D. R. 2002. Antibodies, viruses and vaccines. Nat. Rev. 2:706-713. - PubMed
-
- Carter, P. J. 2006. Potent antibody therapeutics by design. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:343-357. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

