Neurofilaments bind tubulin and modulate its polymerization
- PMID: 19726663
- PMCID: PMC6665525
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1924-09.2009
Neurofilaments bind tubulin and modulate its polymerization
Abstract
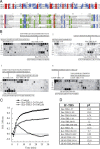
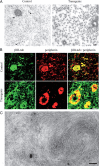
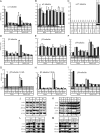
Neurofilaments assemble from three intermediate-filament proteins, contribute to the radial growth of axons, and are exceptionally stable. Microtubules are dynamic structures that assemble from tubulin dimers to support intracellular transport of molecules and organelles. We show here that neurofilaments, and other intermediate-filament proteins, contain motifs in their N-terminal domains that bind unassembled tubulin. Peptides containing such motifs inhibit the in vitro polymerization of microtubules and can be taken up by cultured cells in which they disrupt microtubules leading to altered cell shapes and an arrest of division. In transgenic mice in which neurofilaments are withheld from the axonal compartment, axonal tubulin accumulation is normal but microtubules assemble in excessive numbers. These observations suggest a model in which axonal neurofilaments modulate local microtubule assembly. This capacity also suggests novel mechanisms through which inherited or acquired disruptions in intermediate filaments might contribute to pathogenesis in multiple conditions.
Figures




References
-
- Aamodt EJ, Williams RC., Jr Microtubule-associated proteins connect microtubules and neurofilaments in vitro. Biochemistry. 1984;23:6023–6031. - PubMed
-
- Baas PW, Qiang L. Neuronal microtubules: when the MAP is the roadblock. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:183–187. - PubMed
-
- Baas PW, Vidya Nadar C, Myers KA. Axonal transport of microtubules: the long and short of it. Traffic. 2006;7:490–498. - PubMed
-
- Bartolini F, Gundersen GG. Generation of noncentrosomal microtubule arrays. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:4155–4163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
