Identification of a novel function of PiT1 critical for cell proliferation and independent of its phosphate transport activity
- PMID: 19726692
- PMCID: PMC2781533
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.053132
Identification of a novel function of PiT1 critical for cell proliferation and independent of its phosphate transport activity
Abstract
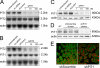
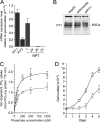
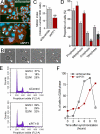
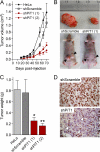
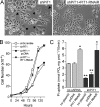
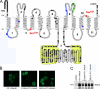
PiT1 is a Na(+)-phosphate (P(i)) cotransporter located at the plasma membrane that enables P(i) entry into the cell. Its broad tissue expression pattern has led to the idea that together with the closely related family member PiT2, PiT1 is the ubiquitous supplier of P(i) to the cell. Moreover, the role of P(i) in phosphorylation reactions, ATP production, DNA structure, and synthesis has led to the view that P(i) availability could be an important determinant of cell growth. However, these issues have not been clearly addressed to date, and the role of either P(i) or PiT proteins in cell proliferation is unknown. Using RNA interference in HeLa and HepG2 cells, we show that transient or stable PiT1 depletion markedly reduces cell proliferation, delays cell cycle, and impairs mitosis and cytokinesis. In vivo, PiT1 depletion greatly reduced tumor growth when engineered HeLa cells were injected into nude mice. We provide evidence that this effect on cell proliferation is specific to PiT1 and not shared by PiT2 and is not the consequence of impaired membrane Na(+)-P(i) transport. Moreover, we show that modulation of cell proliferation by PiT1 is independent from its transport function because the proliferation of PiT1-depleted cells can be rescued by non-transporting PiT1 mutants. PiT1 depletion leads to the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, whereas other MAP kinases and downstream targets of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) remain unaffected. This study is the first to describe the effects of a P(i) transporter in cell proliferation, tumor growth, and cell signaling.
Figures

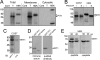
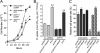

Similar articles
-
Characterization of transport mechanisms and determinants critical for Na+-dependent Pi symport of the PiT family paralogs human PiT1 and PiT2.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):C1377-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00015.2006. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16790504
-
Mapping of the minimal inorganic phosphate transporting unit of human PiT2 suggests a structure universal to PiT-related proteins from all kingdoms of life.BMC Biochem. 2011 May 17;12:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-12-21. BMC Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21586110 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphate (Pi)-regulated heterodimerization of the high-affinity sodium-dependent Pi transporters PiT1/Slc20a1 and PiT2/Slc20a2 underlies extracellular Pi sensing independently of Pi uptake.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 9;293(6):2102-2114. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.807339. Epub 2017 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29233890 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphate and vascular calcification: Emerging role of the sodium-dependent phosphate co-transporter PiT-1.Thromb Haemost. 2010 Sep;104(3):464-70. doi: 10.1160/TH09-12-0814. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20664908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphate transport kinetics and structure-function relationships of SLC34 and SLC20 proteins.Curr Top Membr. 2012;70:313-56. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394316-3.00010-7. Curr Top Membr. 2012. PMID: 23177991 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphate: an old bone molecule but new cardiovascular risk factor.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;77(1):39-54. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12117. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 23506202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphate Transporter Profiles in Murine and Human Thymi Identify Thymocytes at Distinct Stages of Differentiation.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 22;11:1562. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01562. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32793218 Free PMC article.
-
Mice lacking the sodium-dependent phosphate import protein, PiT1 (SLC20A1), have a severe defect in terminal erythroid differentiation and early B cell development.Exp Hematol. 2013 May;41(5):432-43.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Exp Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23376999 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel transport-independent function of PiT1/SLC20A1 in the regulation of TNF-induced apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 5;285(45):34408-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130989. Epub 2010 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20817733 Free PMC article.
-
Slc20a2, Encoding the Phosphate Transporter PiT2, Is an Important Genetic Determinant of Bone Quality and Strength.J Bone Miner Res. 2019 Jun;34(6):1101-1114. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3691. Epub 2019 Mar 19. J Bone Miner Res. 2019. PMID: 30721528 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

